Pulse Documentation - How to
This documentation is still being updated, so you might not find everything you're looking for just yet.
We apologize for any inconvenience this may cause.
If you have any questions or need further assistance, please don't hesitate to contact us or submit a ticket through our service desk.
We're here to help! 😊
Machine states
You will find everything regarding the Machine States module in this chapter.
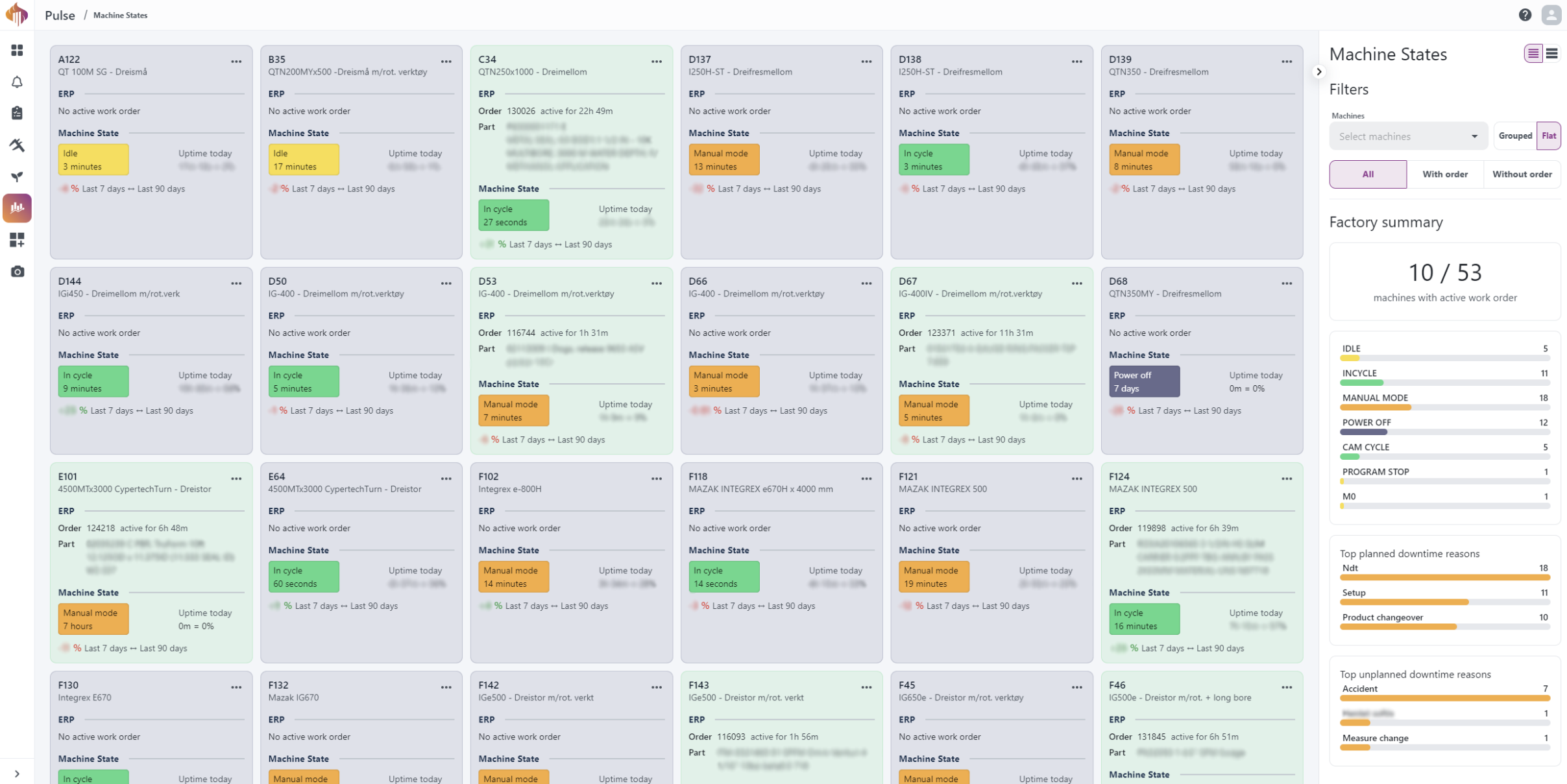
Machine States page
The first page you'll see is the Machine States page. Here you get an overview and a live image of the factory's resources. Each card represents a resource and shows details about ERP data, machine state, and active downtime reasons.
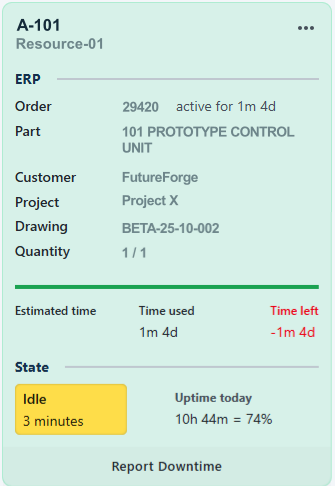
Resource card
This card shows the resource's current state, uptime, and relevant ERP data, including information on currently running work orders. It also contains controls for reporting downtime, including the reason and resolution. Resources with active work orders will appear green.
Sidebar descriptions:The page has a sidebar with filter options and factory summary.
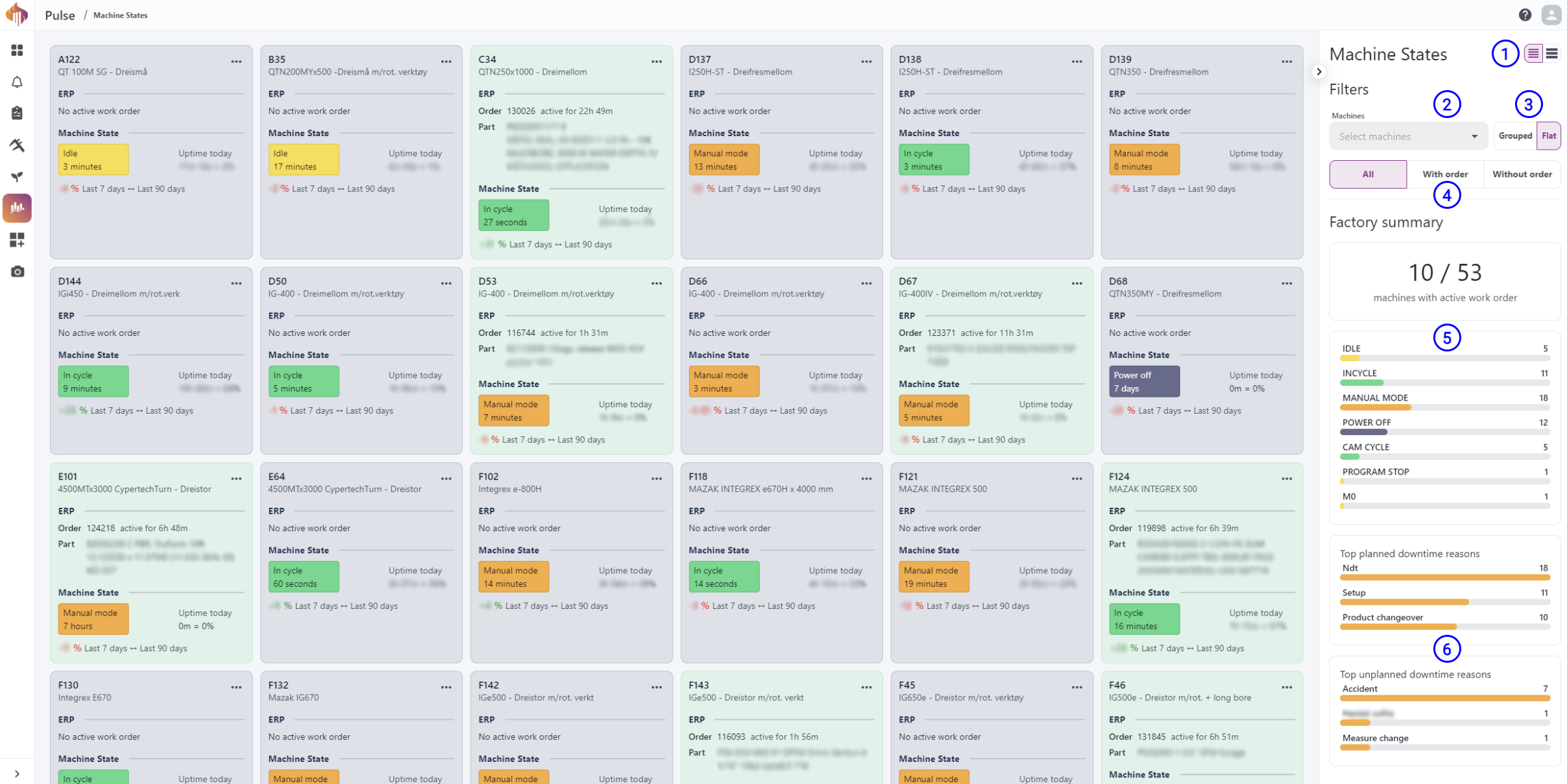
-
Show/hide: Show/hide ERP order details.
-
Machines/Machine Groups: Select specific resources or groups you'd like to display.
-
Grouped/Flat: Select if you'd like to display resources based on groups or not.
-
All/With order/Without order: Display resources according to the selected filter.
-
Machine states overview: Widget displaying the count of all current states registered in the shop.
-
Downtime overview: Two widgets displaying the top planned/unplanned downtime reasons.
Machine Insights
Pressing the triple-dot button in the top-right corner in one of the resources will enable a button called Machine insights.
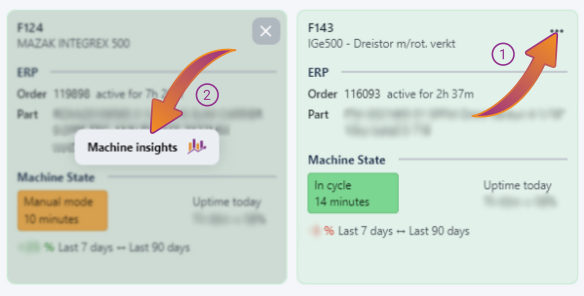
This button opens an overview of the selected resource.
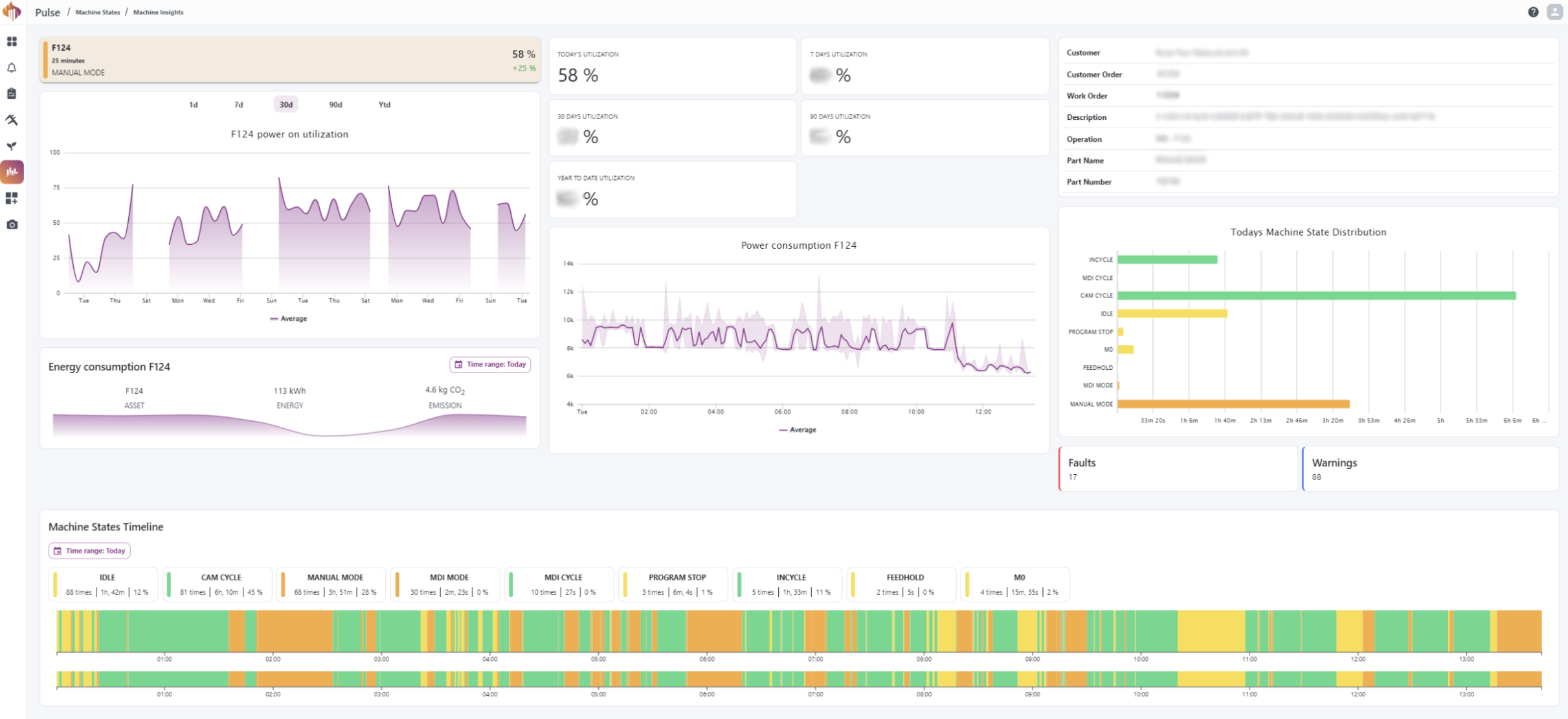
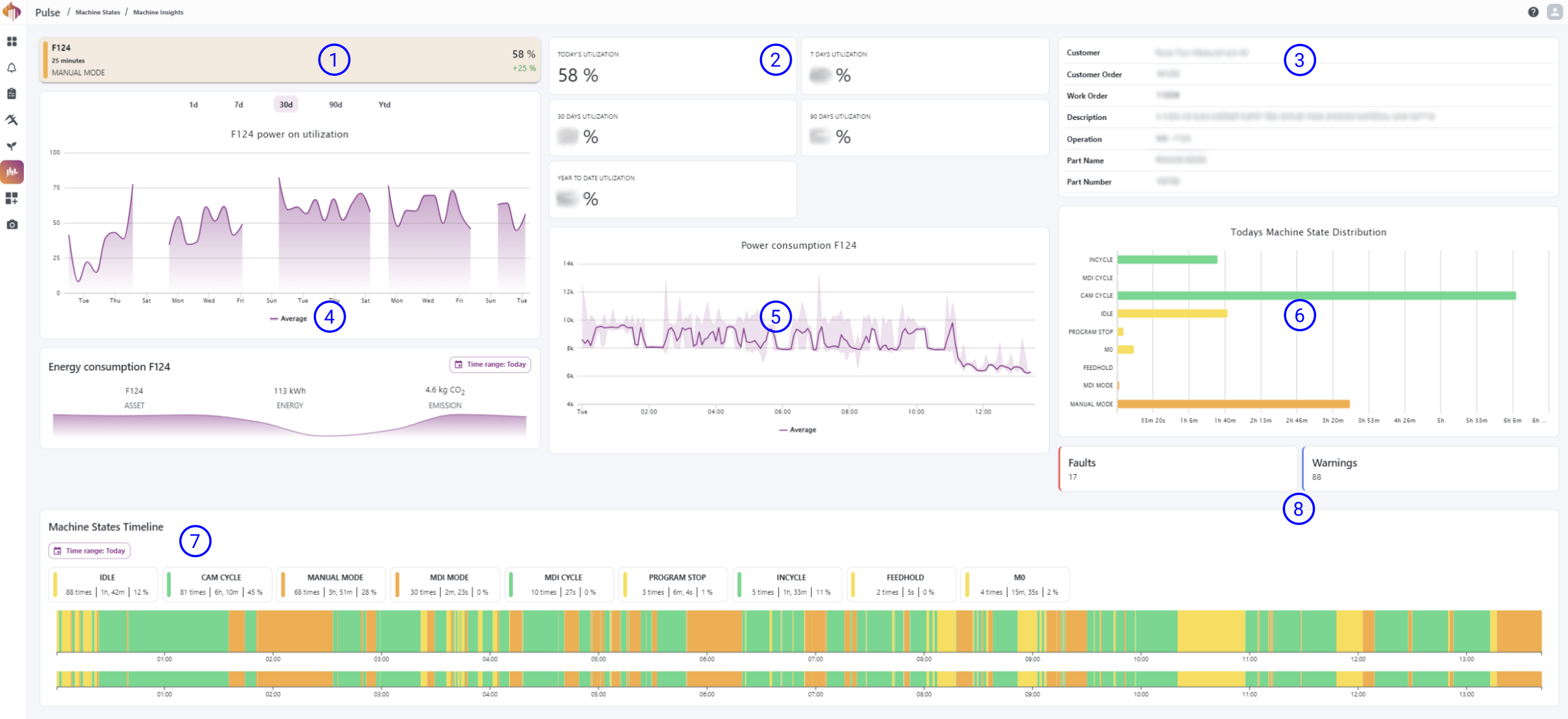
Descriptions:
-
Current state: Shows the current machine state.
-
Utilization percentage groups: A group of calculated utilization percentages.
-
ERP data: Shows information about the current active workorder from the ERP system.
-
Power on utilization graph: Displays the average utilization based on the filters in the banner of the widget.
-
Power consumption: Displays the average power consumption of the selected asset.
-
Today's machine state distribution: A quick overview of the machine state durations from the current day.
-
Resource activity timeline: A timeline showing every machine state, program and workorder events happening during the selected time-range.
-
Faults/Warnings: Shortcut widgets to quickly take you to the Alarm list option in Alarms for the selected resource.
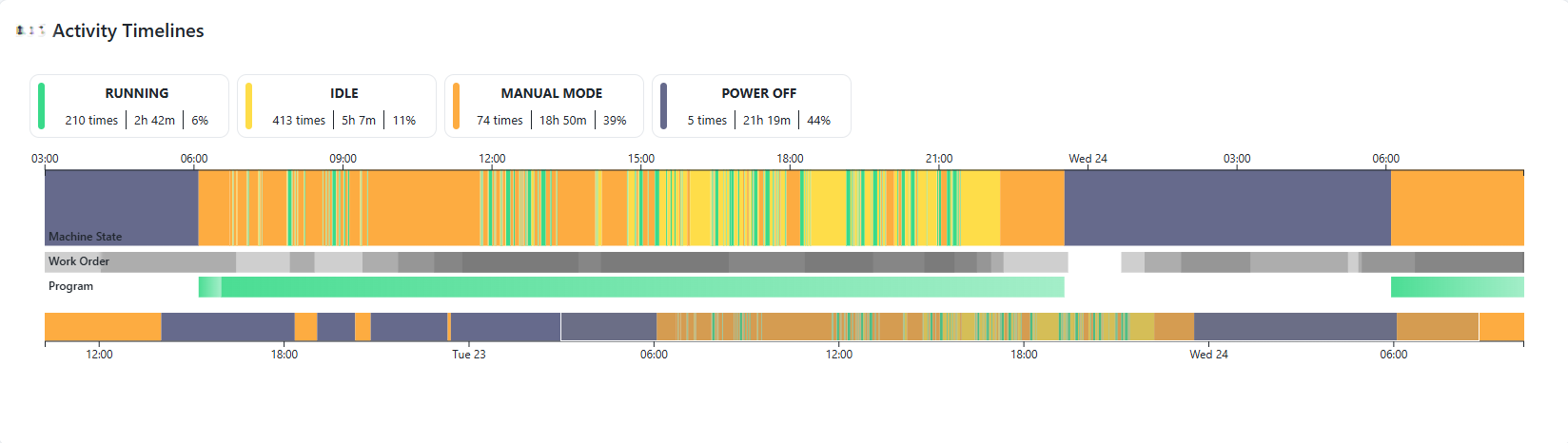
Resource Activity Timeline
The Resource Activity Timeline gives you a visual insight on machine states, workorder and programs for a resource between a timer range. It can be found in Machine Insights or as widget in Workspace.
Notice how you're also able to report a downtime reason through this widget.
The GIF below demonstrates it.
Machine Timelines page
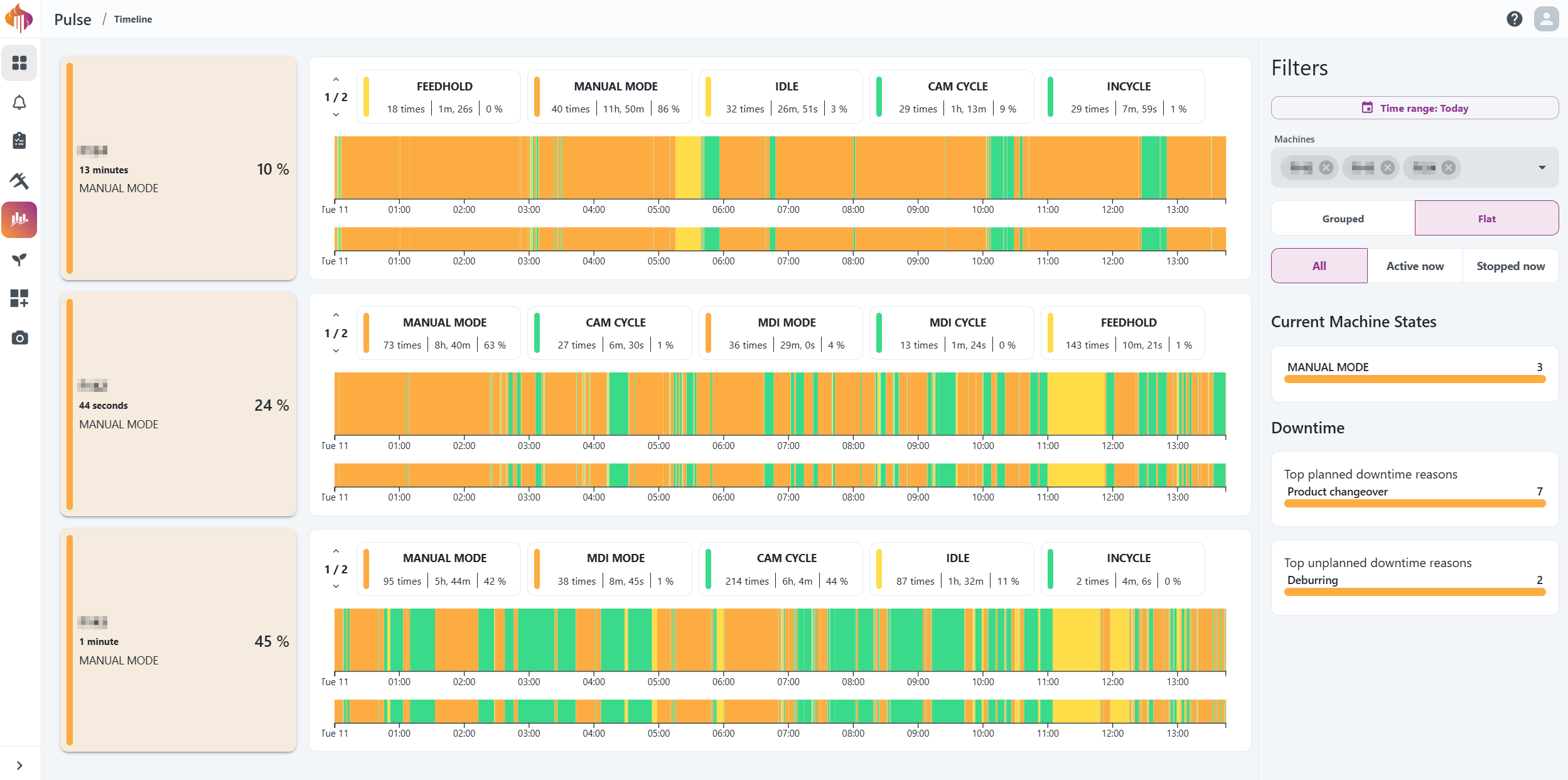
The Machine Timelines page offers a comprehensive overview of the factory's resource machine state timelines.
You can view timelines by individual assets or grouped resources and gain detailed insights into their states, either live, or over a selected time period.
Descriptions:
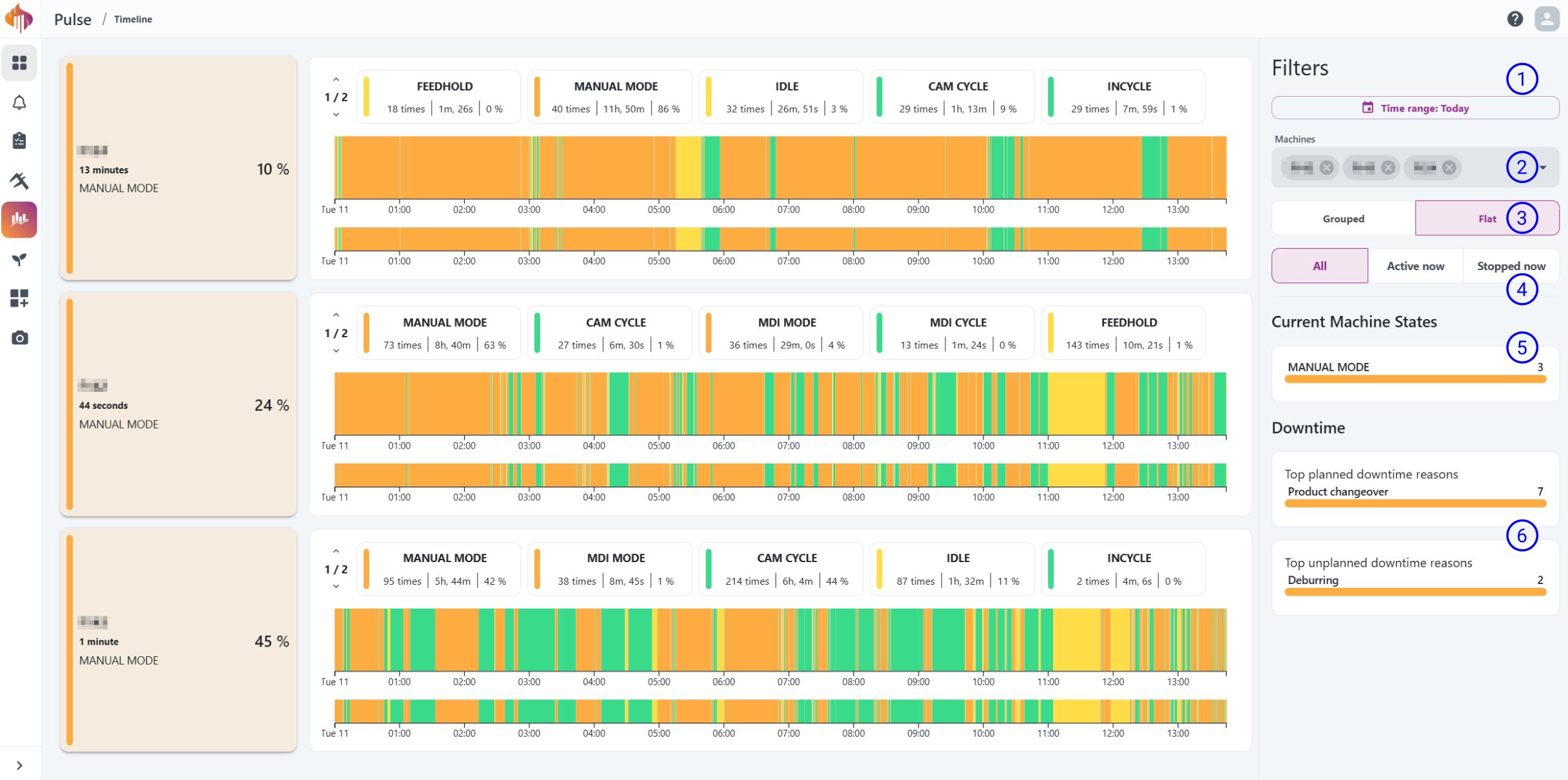
-
Time range: Filter to show the data for the selected timespan.
-
Machines box: Search, and select individual machines or groups to be displayed.
-
Grouped/Flat: Select if you'd like to display resources based on groups or not.
-
All/Active now/Stopped now: Display the filtered machines based on machine state.
-
Current machine states: Shows all the live machine states found in the list of timelines.
-
Downtime: Shows the top planned and unplanned downtime reasons found in the time range defined on point 1.
Utilization Insights

You will find everything regarding the Utilization Insights module in this chapter.
Utilization Insights page
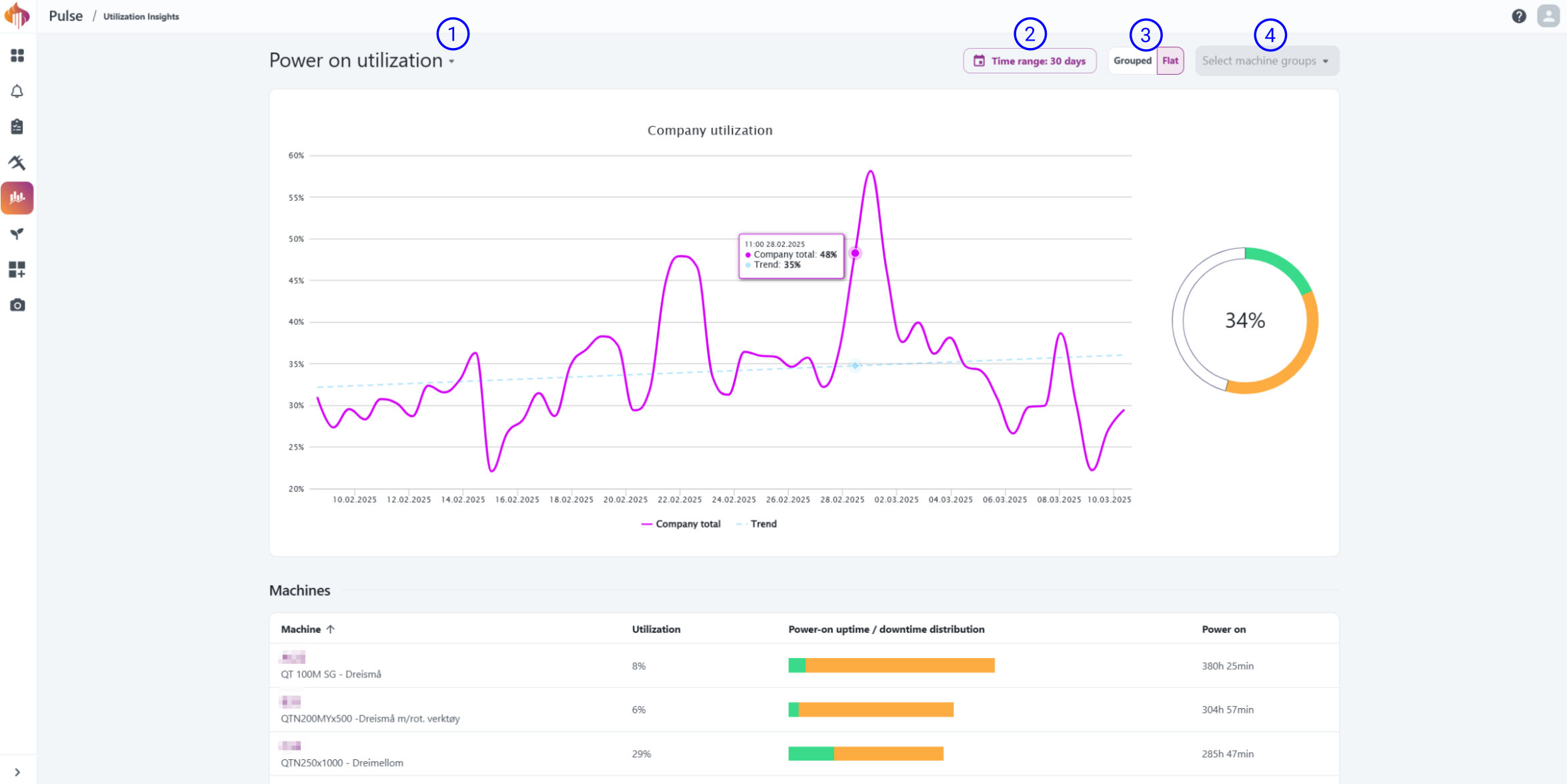
The Utilization Insights page offers an overview over the factory's utilization numbers.
Here you'll be able to see how the factory performs as a whole, by group or by asset and identify trends over time.
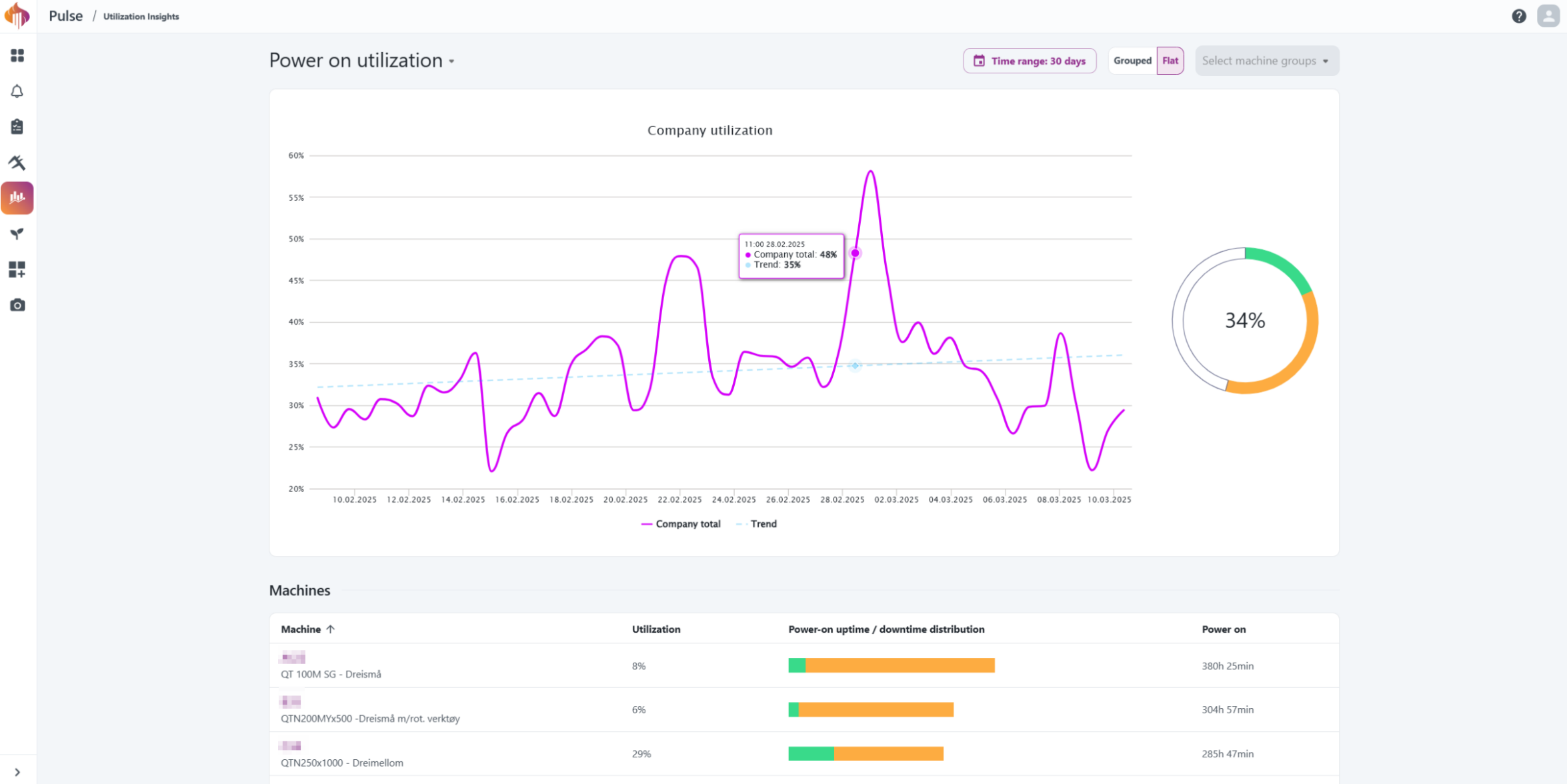
Descriptions:
Utilization calculation methods
We currently provide four methods for displaying utilization data, with a fifth option under development and coming soon.
Below, these methods are explained in detail.
Power-on utilization
This metric reflects how efficiently the machine is used while operational, and does not account for periods when the machine was turned off or its overall capacity.
Example:
"Sample CNC Machine" has been operational for 8 hours a day between January and May. During this period, the Power-on utilization numbers are very good.
Here’s a figure illustrating the Power-on utilization:
However, when the same data is analyzed in a 24/7 context, the utilization numbers change significantly:
The following section provides more details about 24/7 utilization.
24/7 utilization
This metric considers the entire day, including periods when the machine was powered off, providing a broader view of its overall usage. For example, as shown in the figure above, the 24/7 utilization numbers for Sample CNC Machine are lower, because the machine was only operational for 8 out of 24 hours each day.
Active-order utilization
This method is currently under development and will be available soon.
This metric focuses on the alignment between machine usage and active job assignments, providing a detailed view of operational efficiency linked to ERP-driven workflows. Unlike power-on utilization, which includes all powered-on time, active-order utilization specifically excludes periods when no one was clocked into an order, even if the machine was running or ready to operate.
Machine Capacity utilization (OEE)
OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) represents how effectively a machine produces during the time it was scheduled to run, according to the Machine calendars.
Formula
- Availability = Uptime ÷ Planned Production Time
- Performance = (Ideal Cycle Time × Total Pieces) ÷ Operating Time F
- Quality = Good Pieces ÷ Total Pieces
Example calculation
⚠️ Note: In systems where Performance and Quality values are available, the OEE calculation will include them. When these values are not provided, they are automatically set to 100%, meaning OEE effectively reflects Availability.
ℹ️ Availability here is based on the machine’s Capacity settings.
💡 Important for admins:
Very low capacity values (e.g., 0.1 h) can cause extremely high utilization spikes in Machine Capacity charts if production occurs on those days.
To avoid distorted results, set non-production days (like weekends) to 0 h instead of small fractional values.
This metric shows how well a machine's production met the planned capacity time, filtering out time you intentionally didn’t plan to run.
Factory Calendar utilization (OOE)
OOE (Overall Operations Effectiveness) measures effectiveness against the entire scheduled calendar window (Factory calendar). It answers the question: “Out of all the time that was scheduled in the calendar, how much effective production did we achieve?”
Formula
- Availability = Uptime ÷ Calendar Time
- Performance = (Ideal Cycle Time × Total Pieces) ÷ Operating Time
- Quality = Good Pieces ÷ Total Pieces
Example calculation
⚠️ Note: In systems where Performance and Quality values are available, the OEE calculation will include them. When these values are not provided, they are automatically set to 100%, meaning OEE effectively reflects Availability.
ℹ️ Availability here is based on the Factory Calendar settings.
This metric shows how well production utilized the entire factory calendar time, including periods you intentionally planned as downtime. As a result, OOE values are typically lower than OEE in environments with many scheduled stops.
Comparison of utilization methods
The figure below highlights how the three utilization methods - Power-on utilization, 24/7 utilization, and Active-order utilization, differ in focus and scope. Each provides unique insights into machine efficiency, from operational hours to full capacity usage and task-specific performance.
Downtime reasons
Downtime refers to any period when a resource is unavailable or not operational, impacting productivity.
To track and analyze these interruptions, users can report downtime reasons in two ways, both shown in this chapter.
Additionally, we provide a dedicated Downtime report for deeper insights into all reported downtime reasons within the selected time range.
Downtime reasons can be configured in the Admin settings of Ignos.io. This option is only available to Admins and can be accessed from the bottom-left corner if you have the Admin role.
Report through the Resource Activity Timeline
Select which machine state or work order you want to report a downtime reason for. In the dialog, you can adjust the start and end time, select a downtime reason, and add an additional comment.
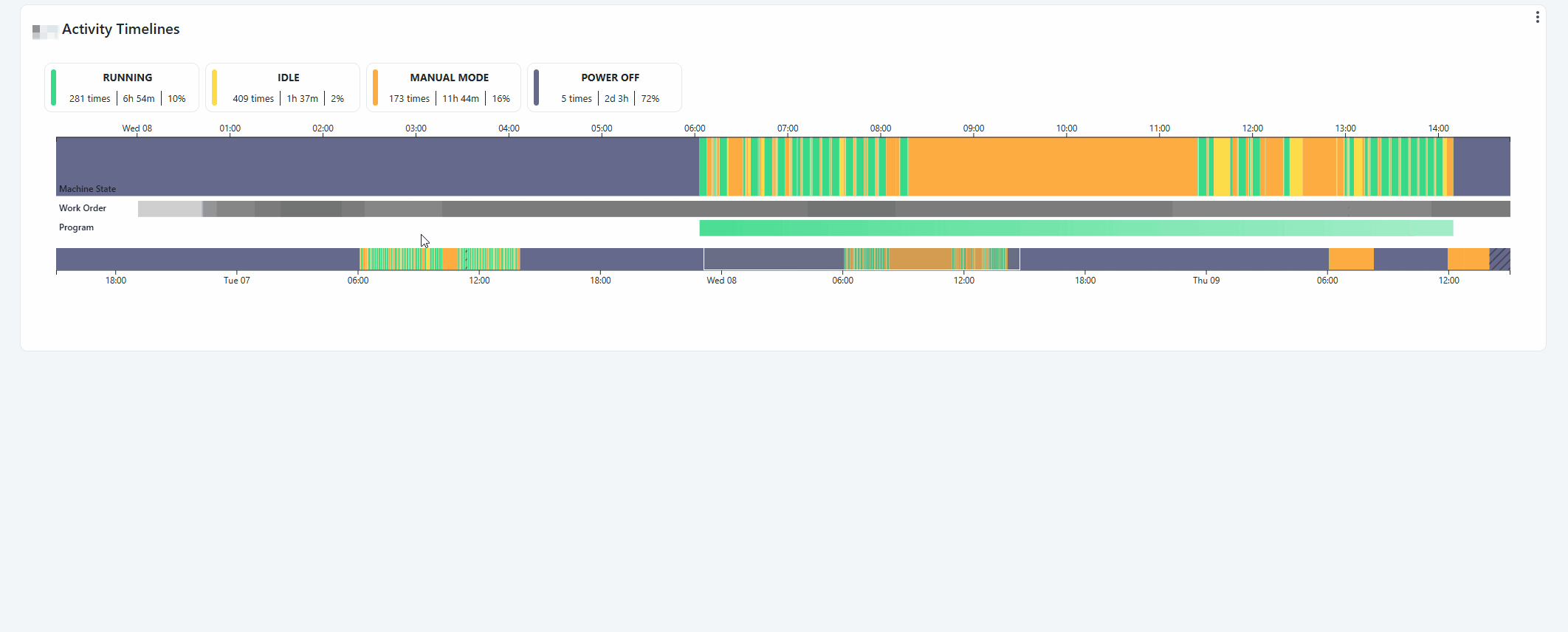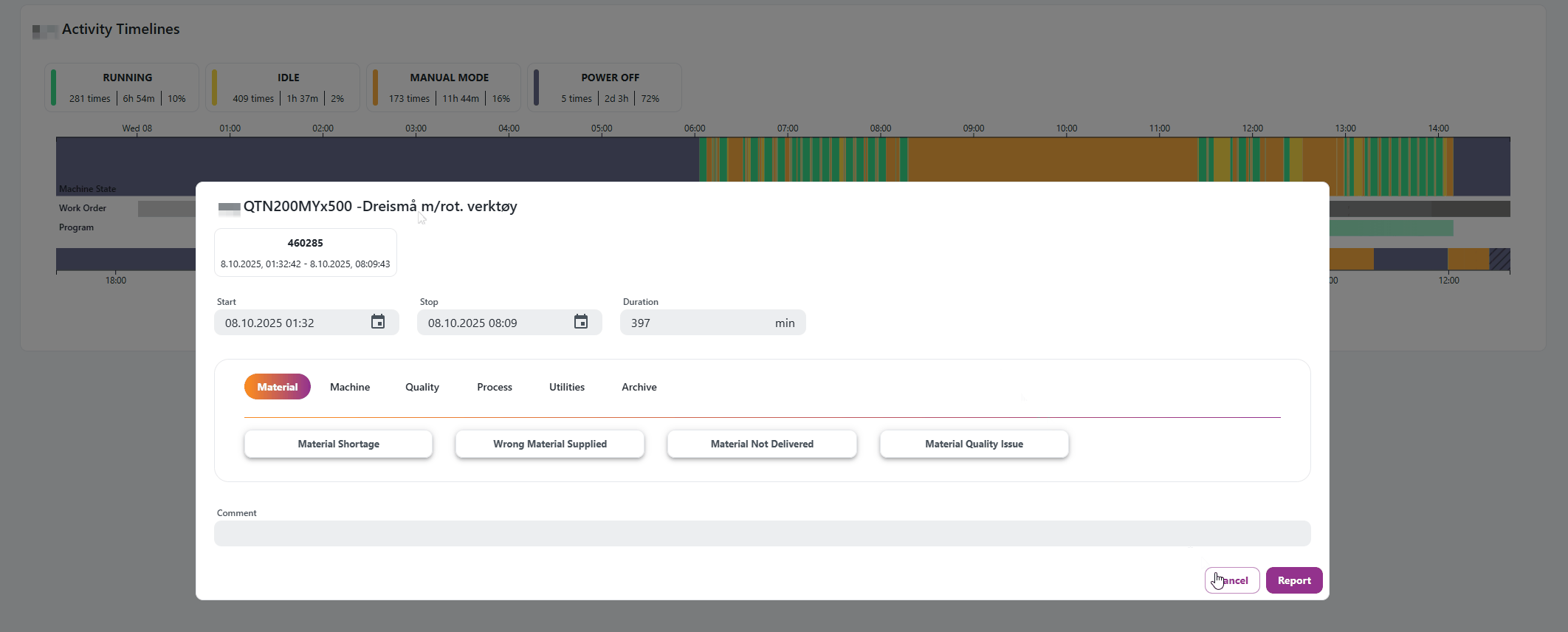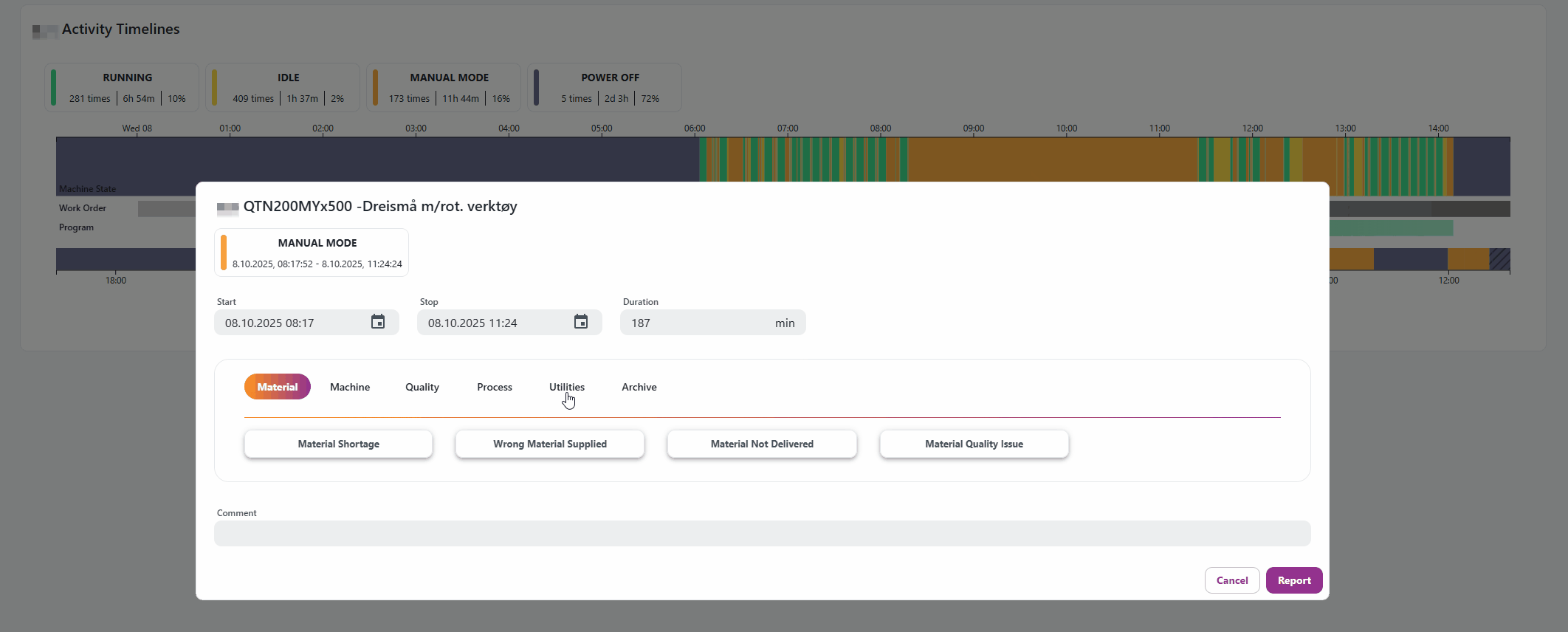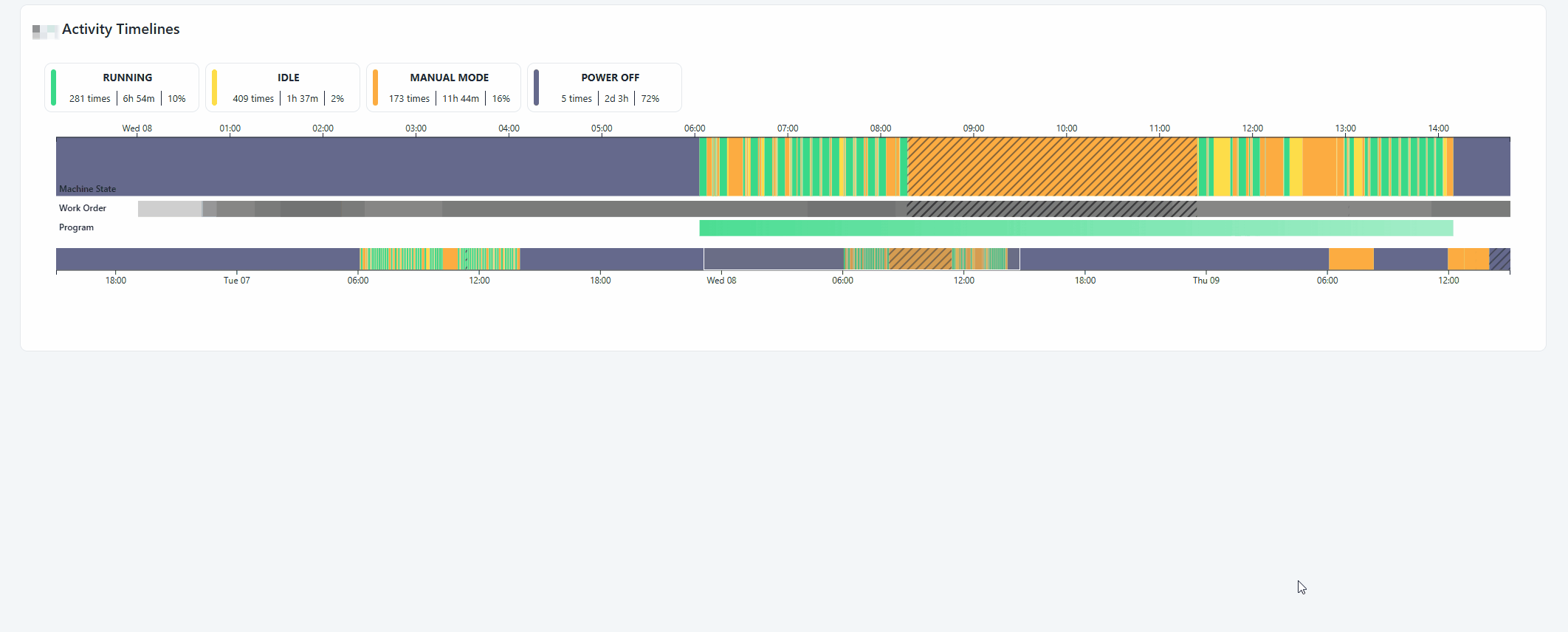
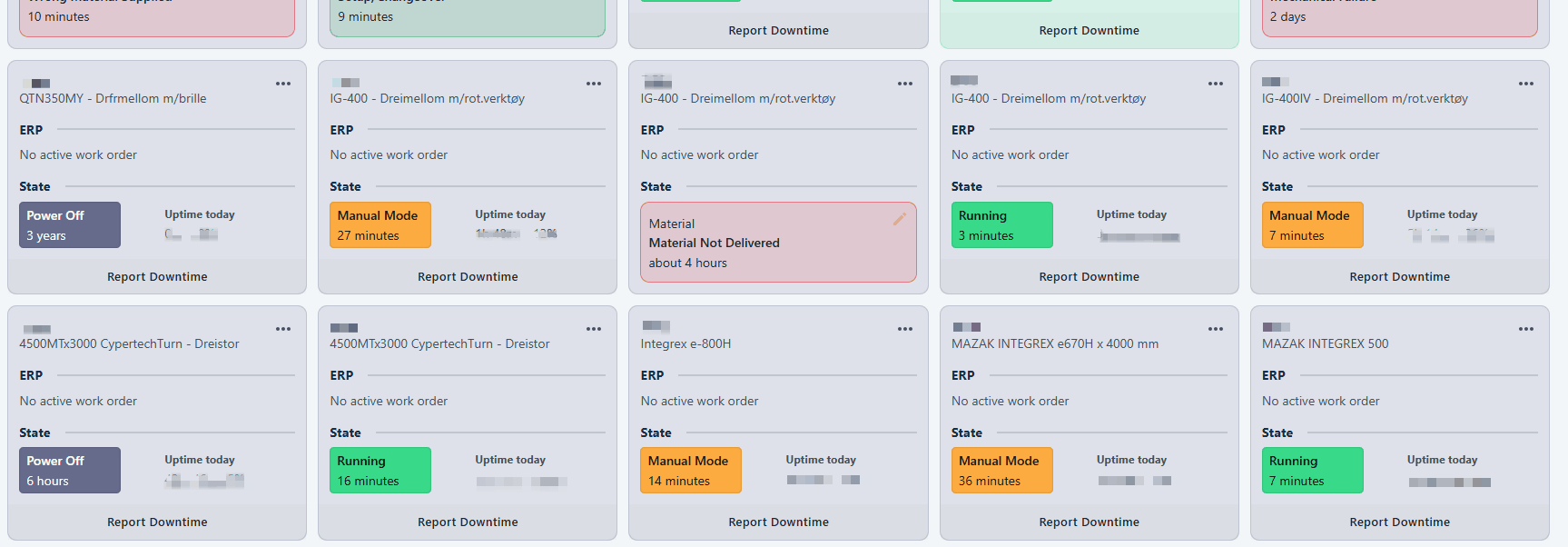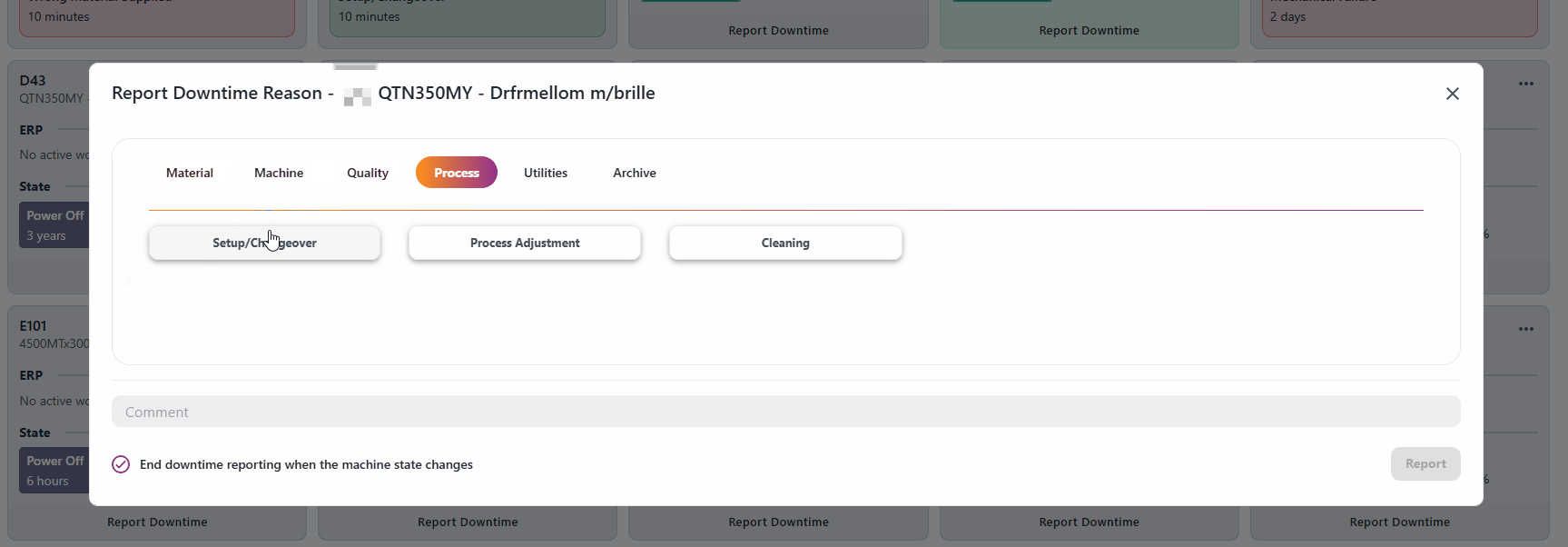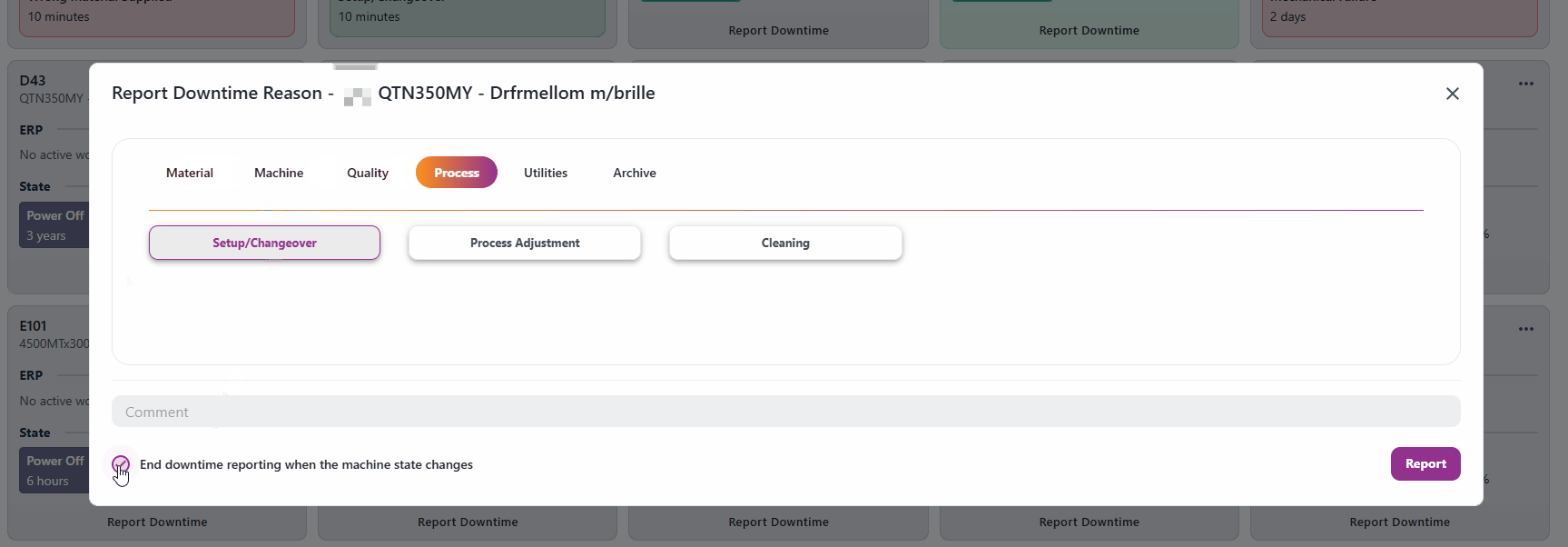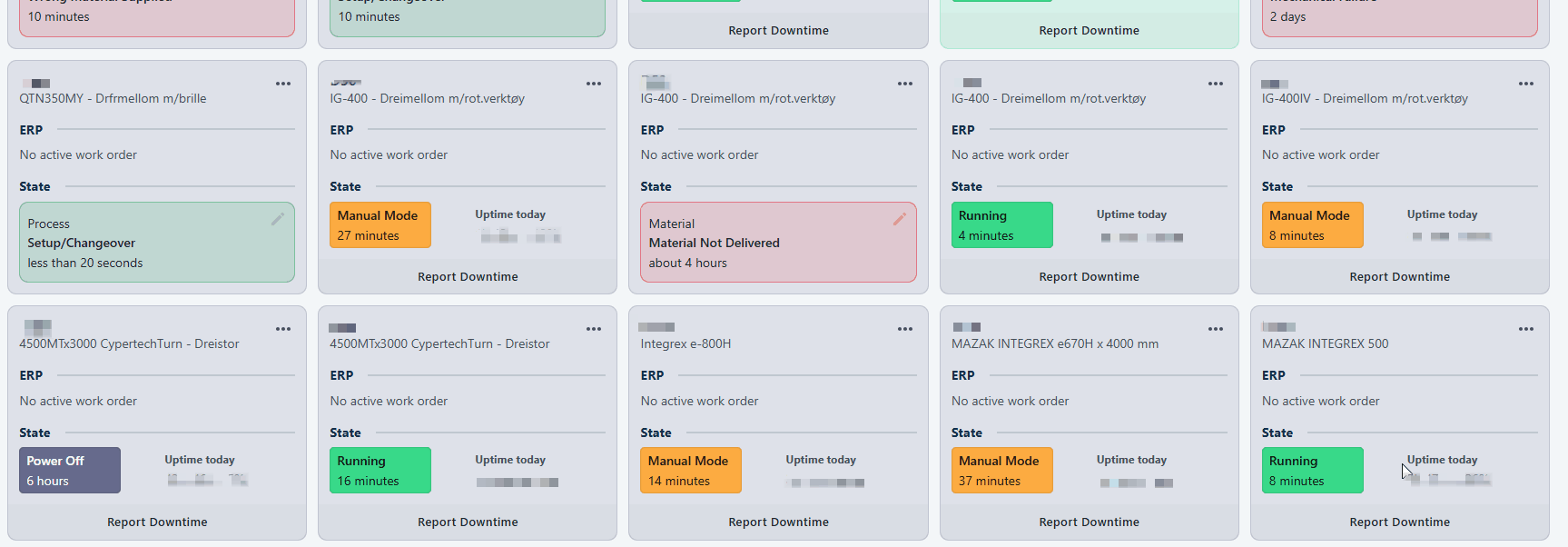
Report through Machine States
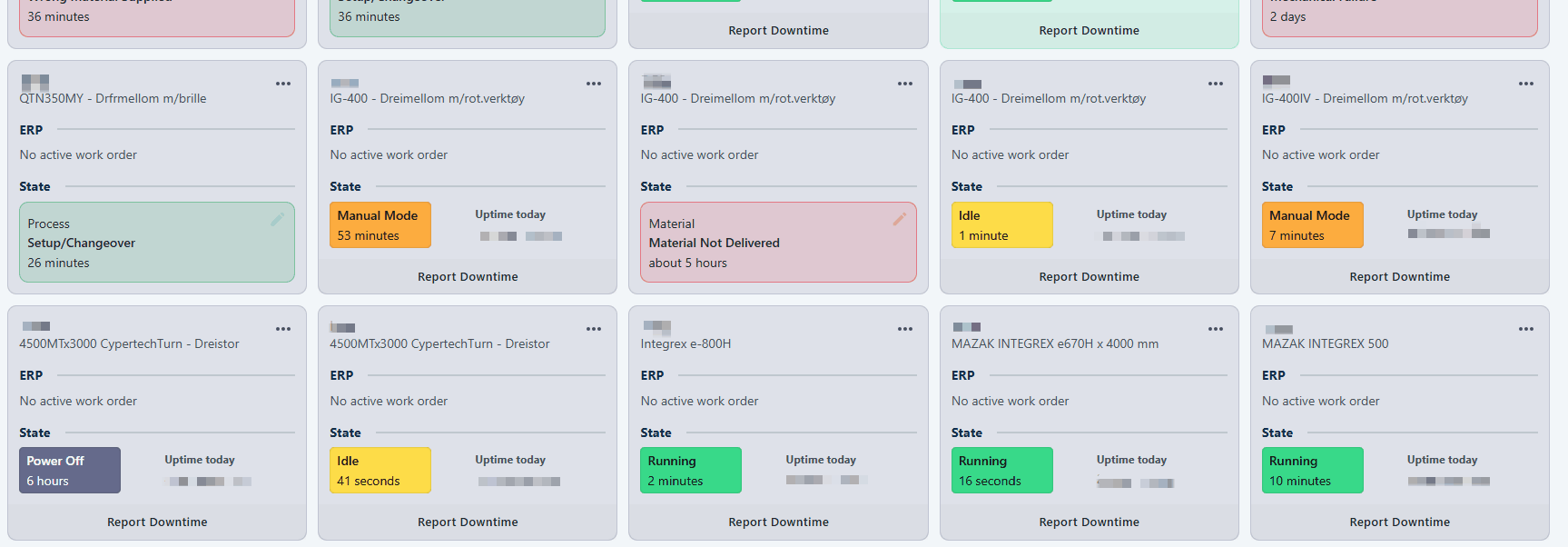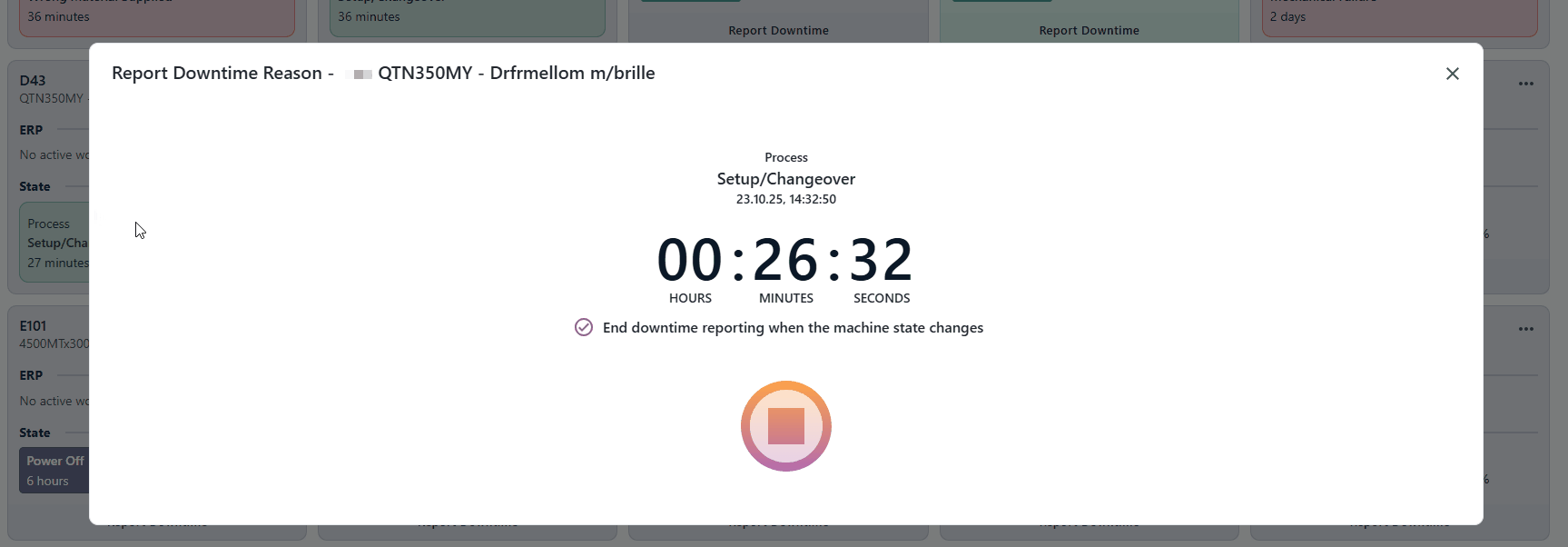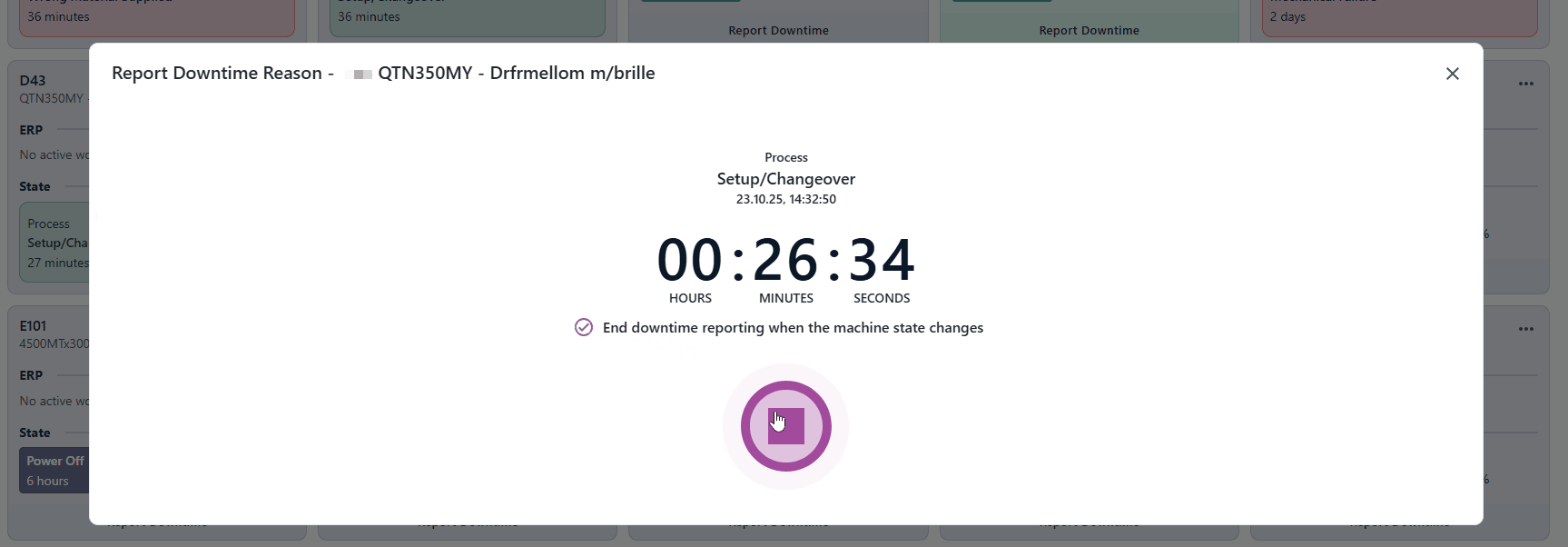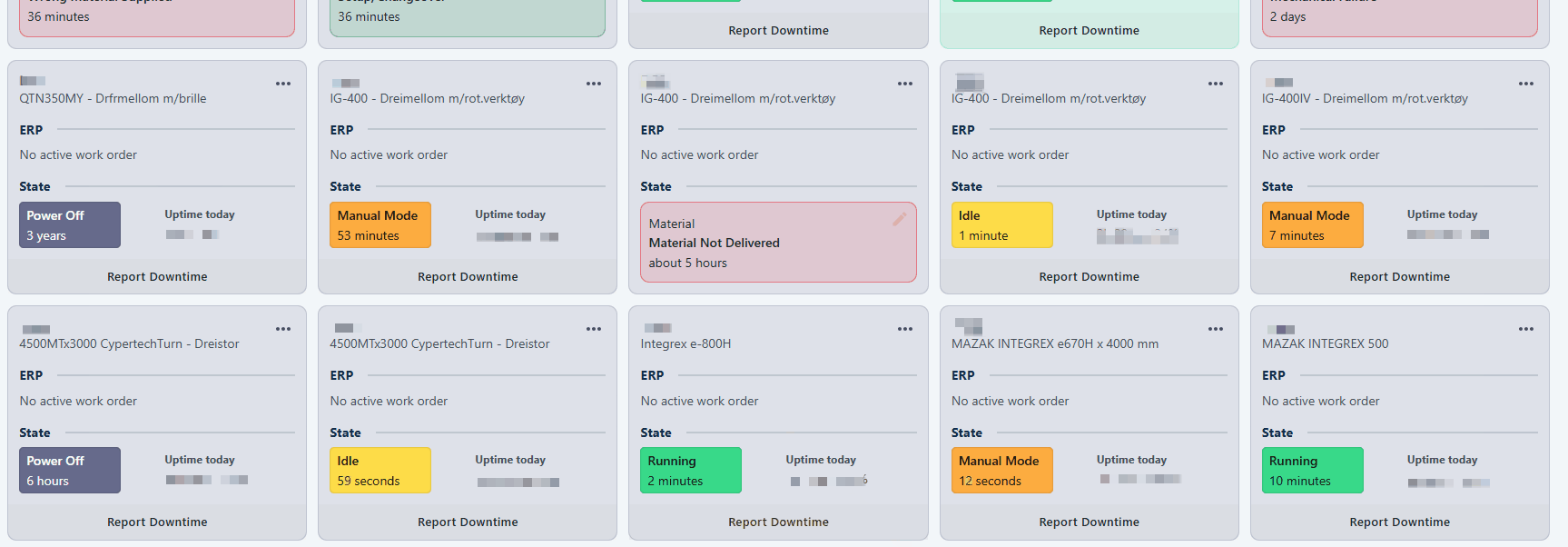
Click "Report Downtime" at the bottom of relevant Resource card. Select a downtime reason, additional comment and if it should follow the machine state if available.
Resources with machine states will give you the opion "End downtime reporting when the machine state changes". If this is enabled, the reporting will end automatically when the machine state changes.
Resources that have active downtime reports will display a marker.
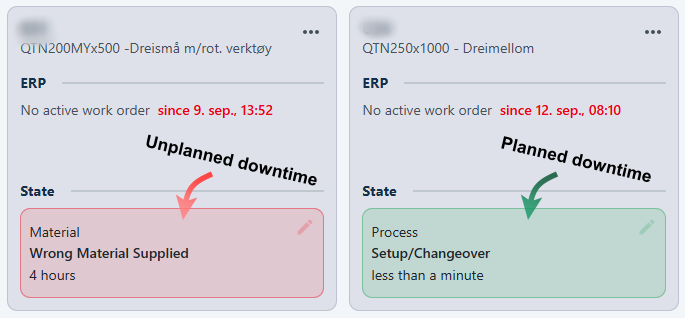
You can easily end or edit active downtime reporting by clicking the downtime report marker and pressing the stop button or checking/unchecking the "End downtime reporting when the machine state changes" option.
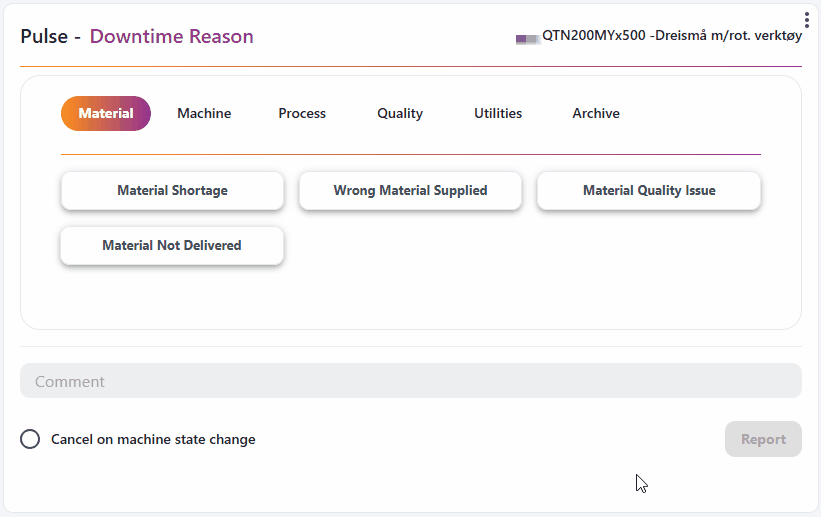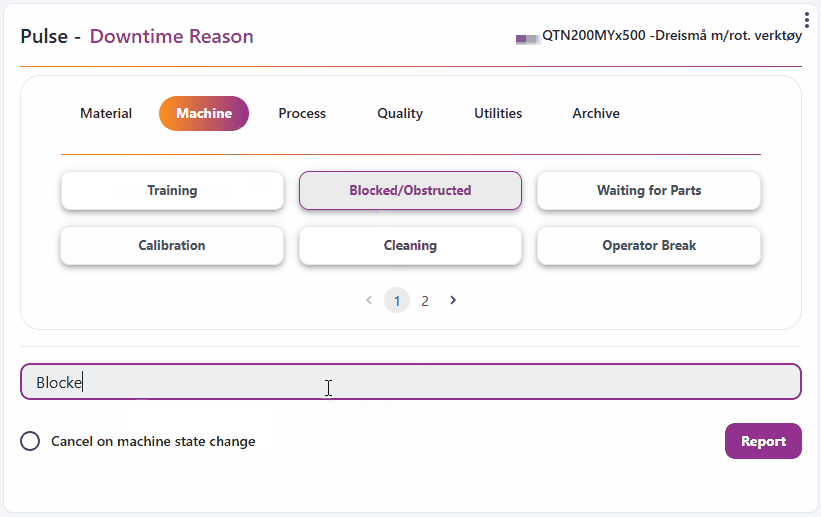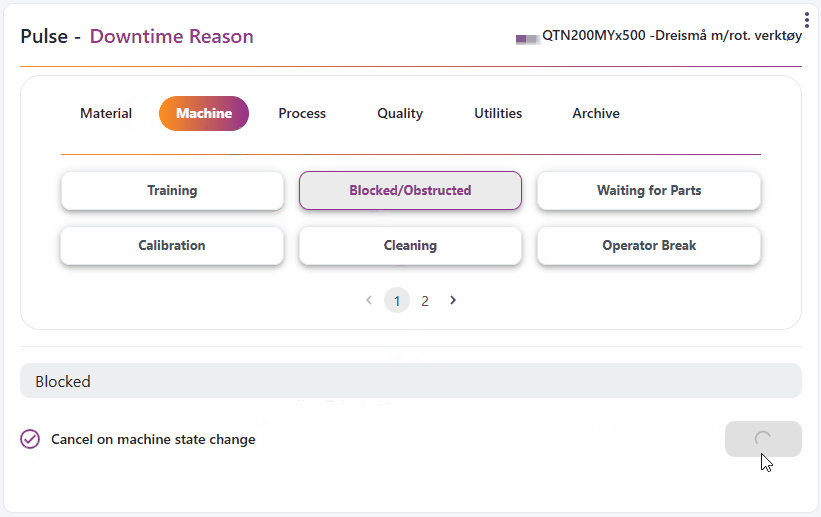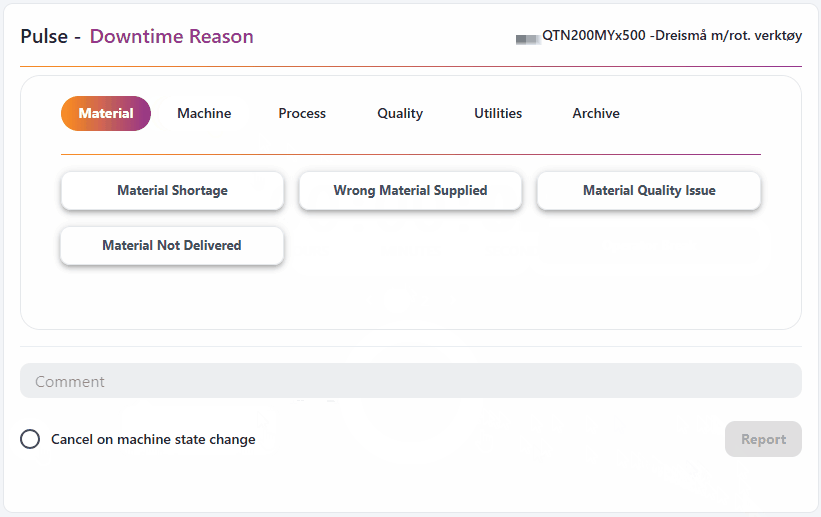
Report through the Downtime Reason widget in Workspace
The Downtime Reason widget in Workspace allows the user to very easily report downtime.
More info about this widget can be found in its own chapter.
How to report:
Downtime Report
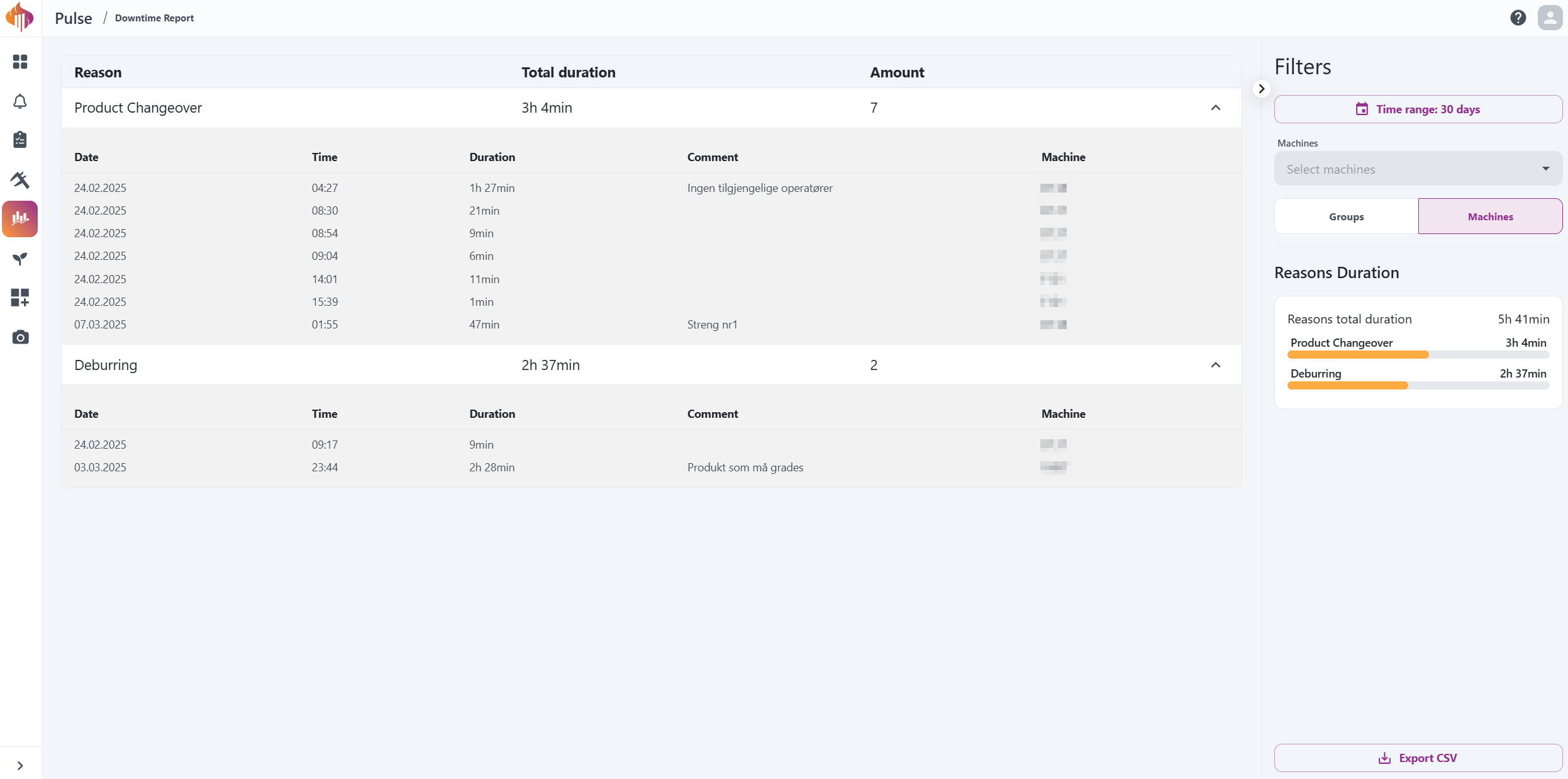
The Downtime Report gives deeper insights into the duration of all reported downtime reasons. You're also able to Export CSV from this page from the bottom of the right-margin.
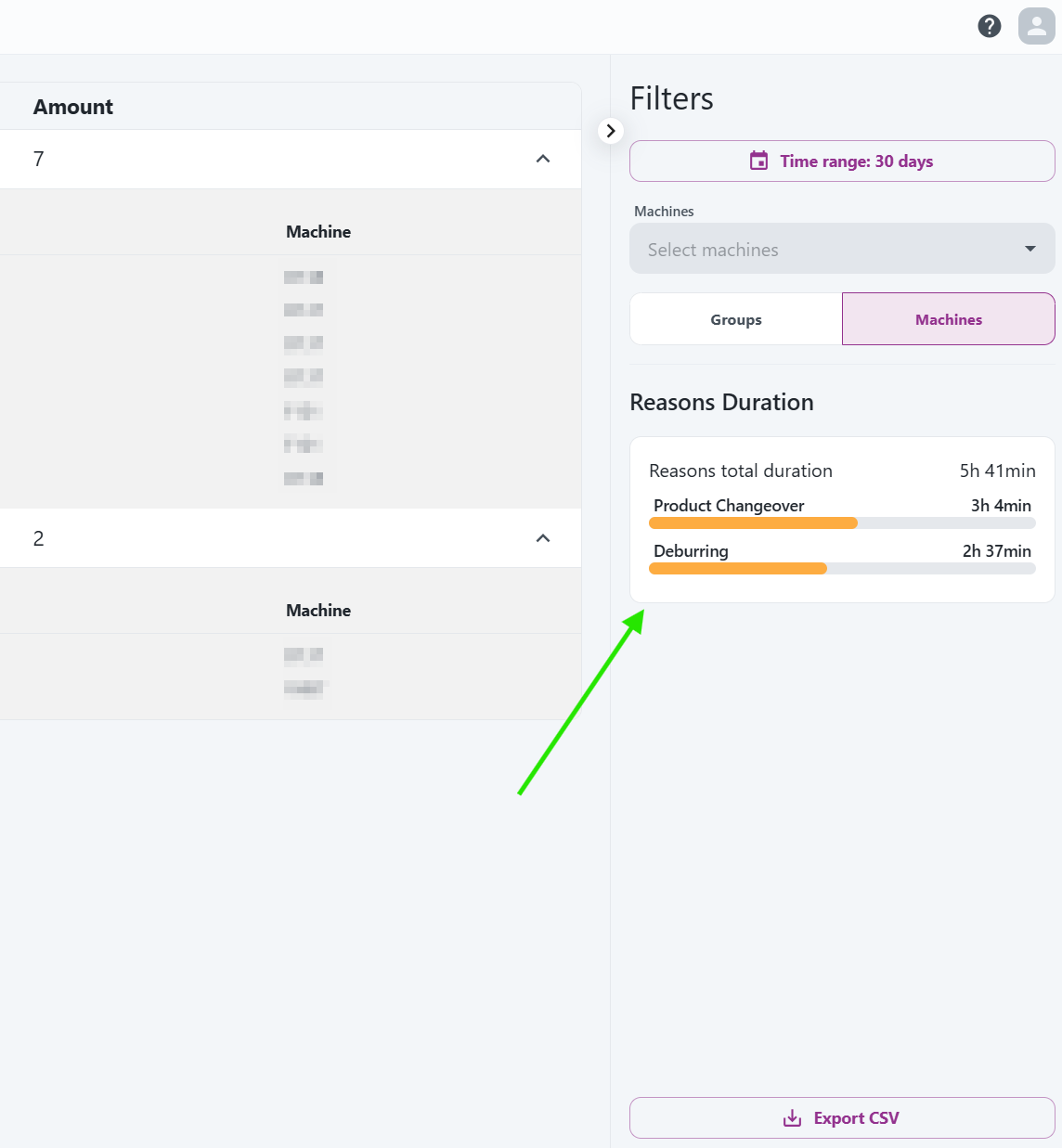
In the mentioned margin found on most pages in the Pulse app you will also have the Top planned and Top unplanned downtime reasons displayed:
Downtime Reasons settings
Downtime reasons can be configured in the Admin settings of Ignos.io. This option is only available to Admins and can be accessed from the bottom-left corner if you have the Admin role.
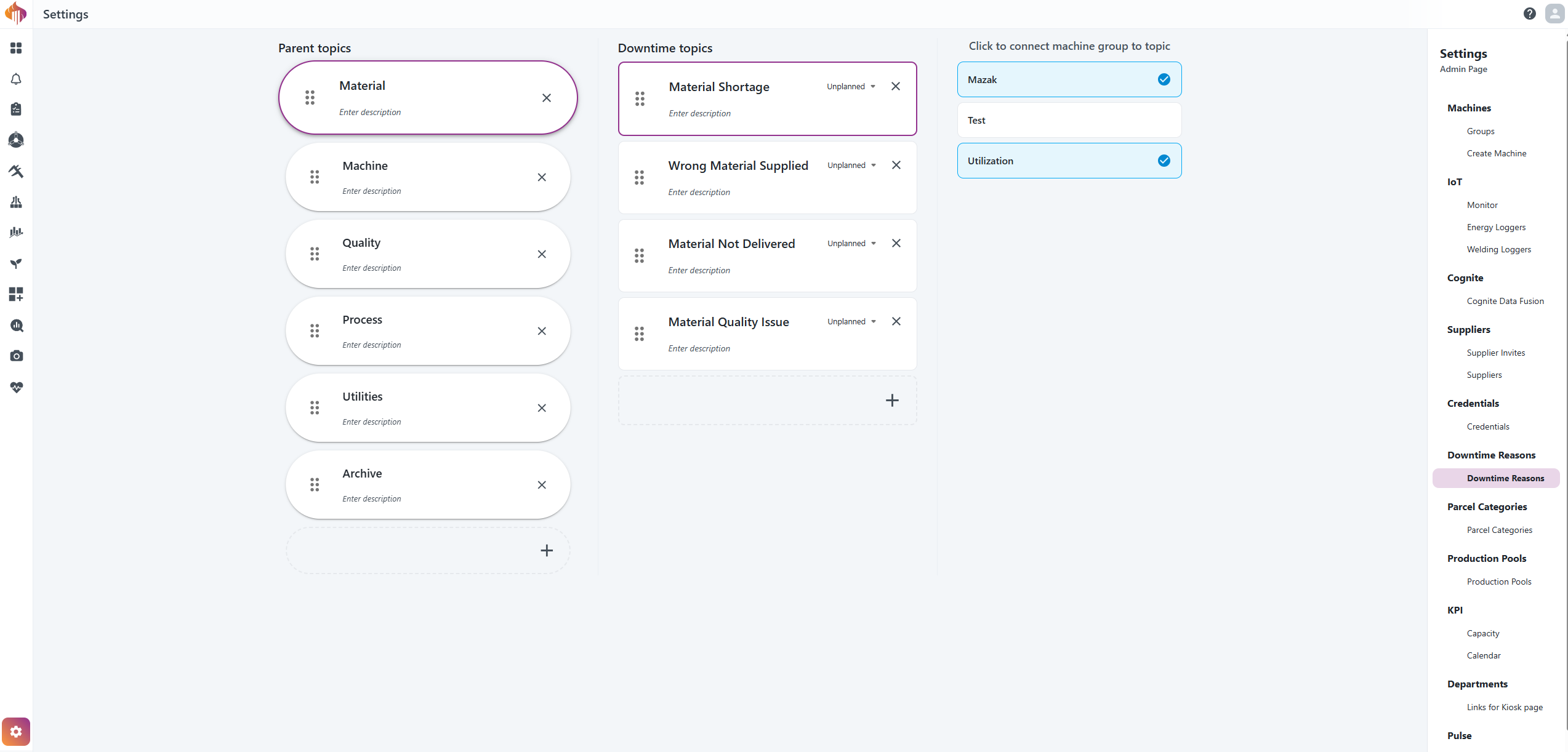
Descriptions:
-
Parent topics: Add parent topics as needed (see point 8). Select a Parent Topic by clicking on a parent topic card to view its associated Downtime topics. The selected card will be highlighted, and the Downtime topics list will update to the left.
-
Downtime topics: Add downtime topics linked to the selected parent topic as needed (see point 8). Select a Downtime Topic by clicking on a Downtime Topic card to view its associated Machine Groups. The selected card will be highlighted, and the Machine Groups list will update to the left.
-
Machine group: Link selected Downtime topics to a machine group. The downtime reasons will appear when reporting Downtime Reasons on resources that are linked to selected machine groups
-
Description: Provide additional context for the defined topic. This will appear as a tooltip when hovering over the topic while reporting:
-
Planned/Unplanned: Specify whether the Downtime Topic should be categorized as Planned or Unplanned.
-
Sorting: Click and hold the drag handle next to an item to sort the order of the topics via drag-and-drop.
-
Delete topic: Press the x icon inside the box to delete a topic.
-
Add more topics: Click the plus-button to add more topics.
Pulse Widgets for Workspace
You will find everything Pulse-related regarding the Workspace module in this chapter.
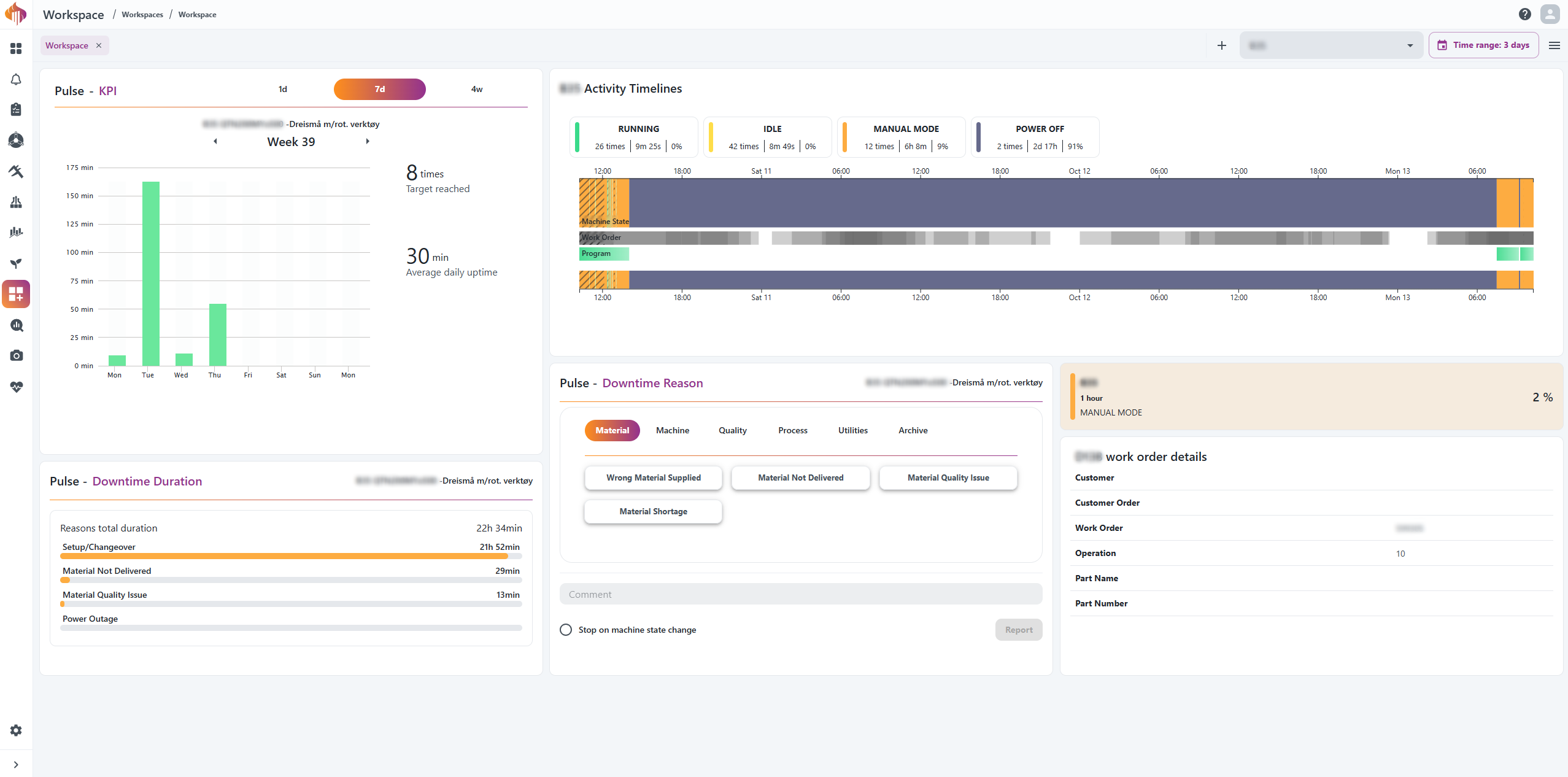
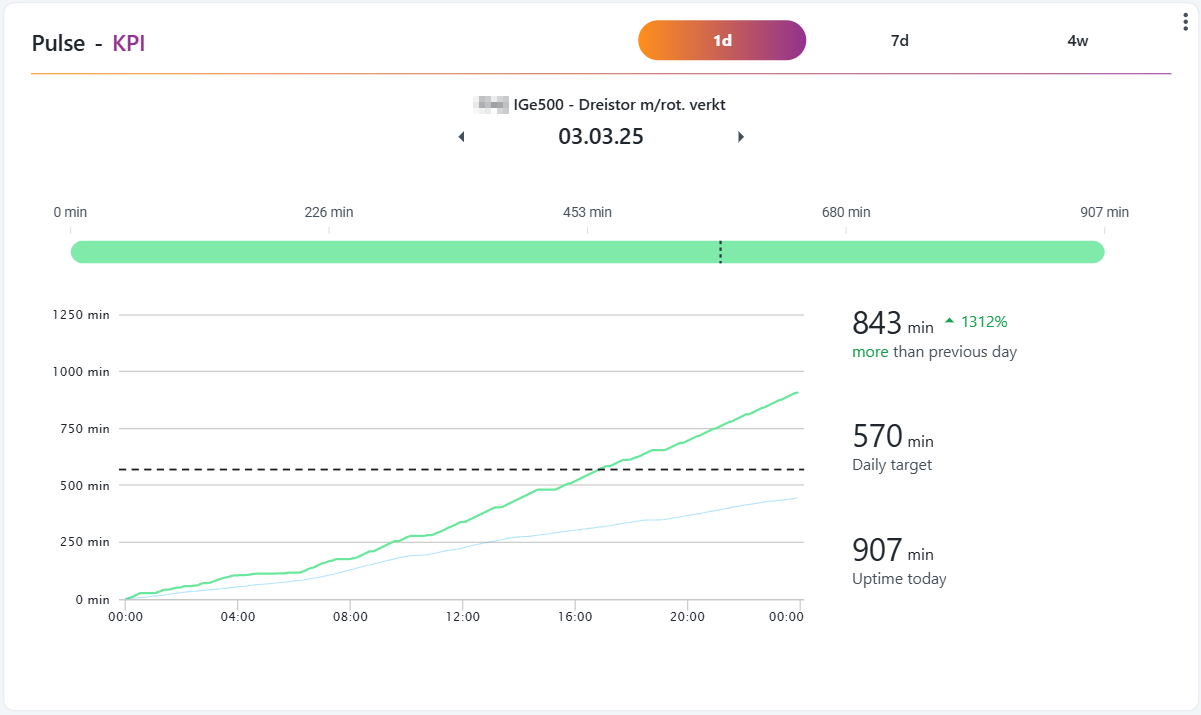
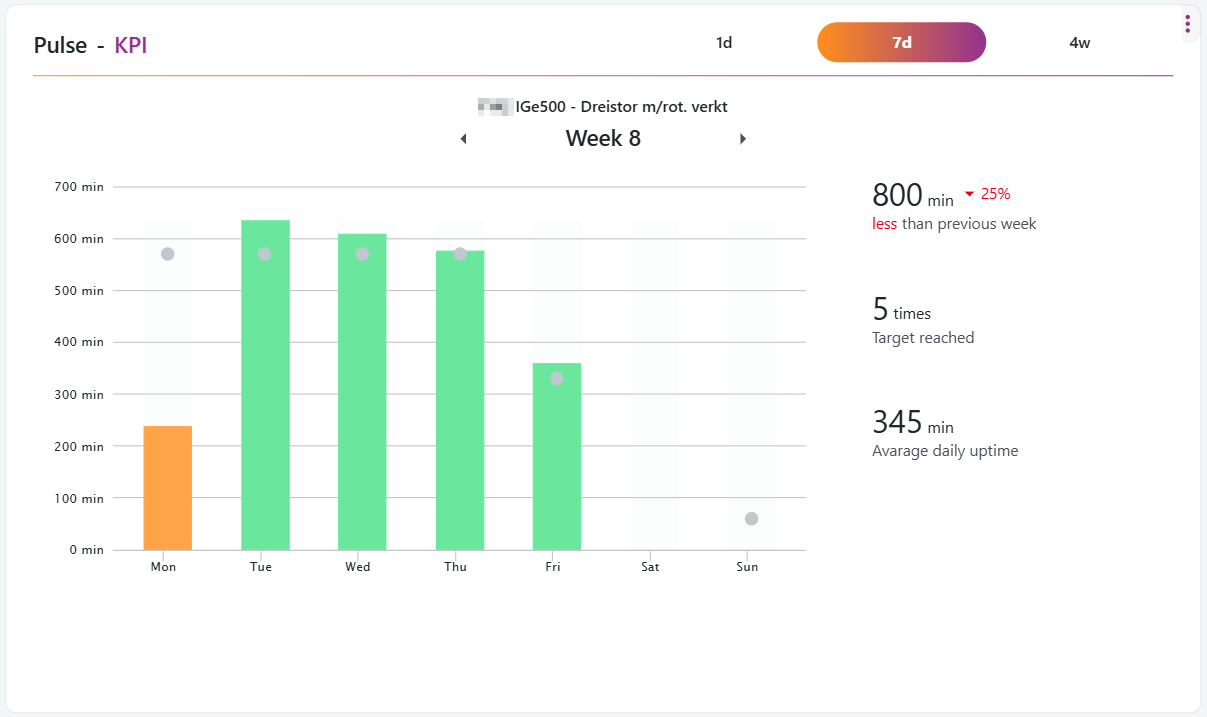
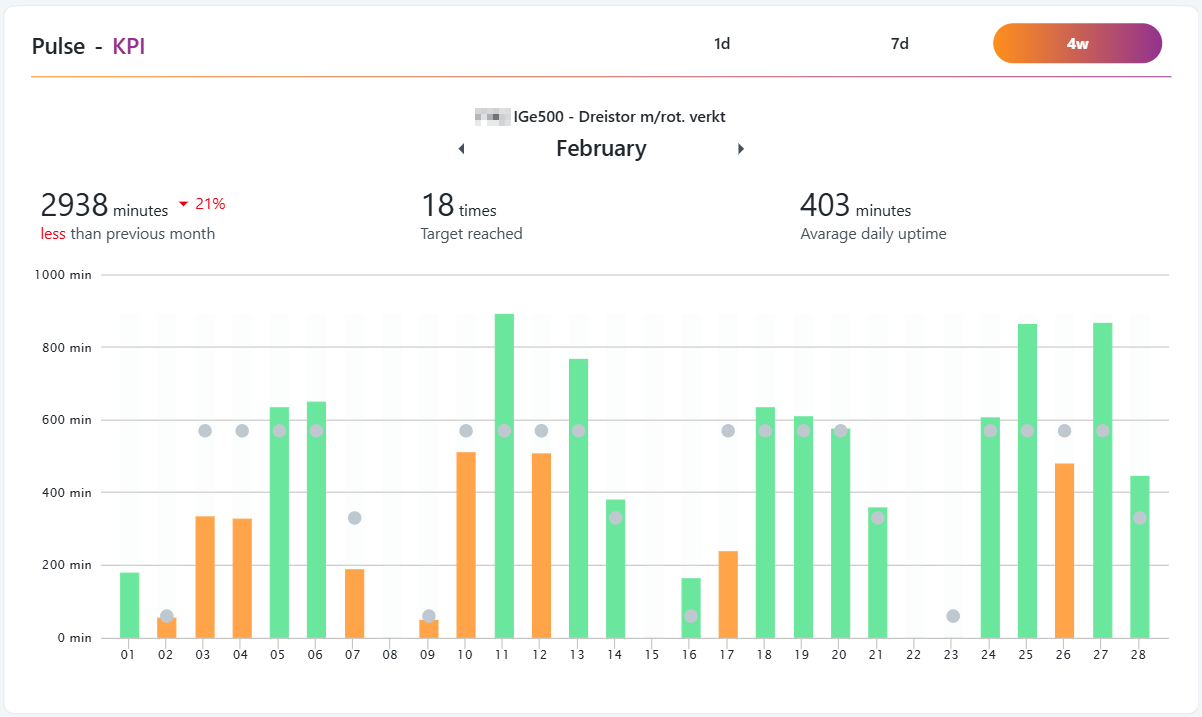
KPI widget
The KPI widget is very much inspired by modern fitness trackers.
This widget works very similar to a step-counter. It counts only the uptime and has a daily target-uptime, based on the capacity defined in the Ignos.io settings. The user can deep-dive back in time, and display each day in either of three formats: 1d (1 day), 7d (1 week) or 4w (1 month).
Capacity settings
Capacity settings is only available for Admins and can be accessed in the bottom-left corner if you have the Admin role.
Admins can set capacity either by individual days, or as a flat value. We'll explain this in more detail below the screenshot.
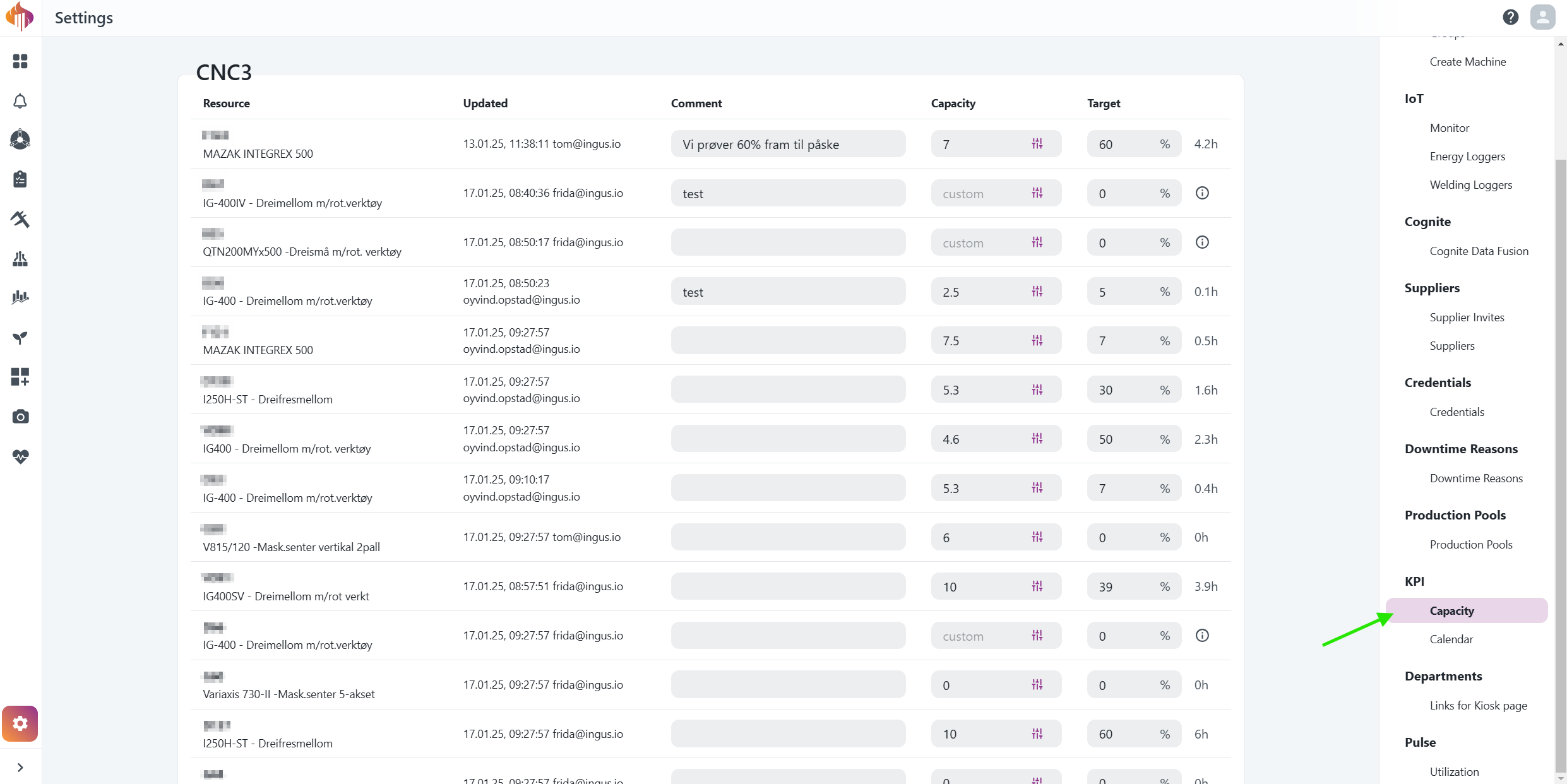
Descriptions:
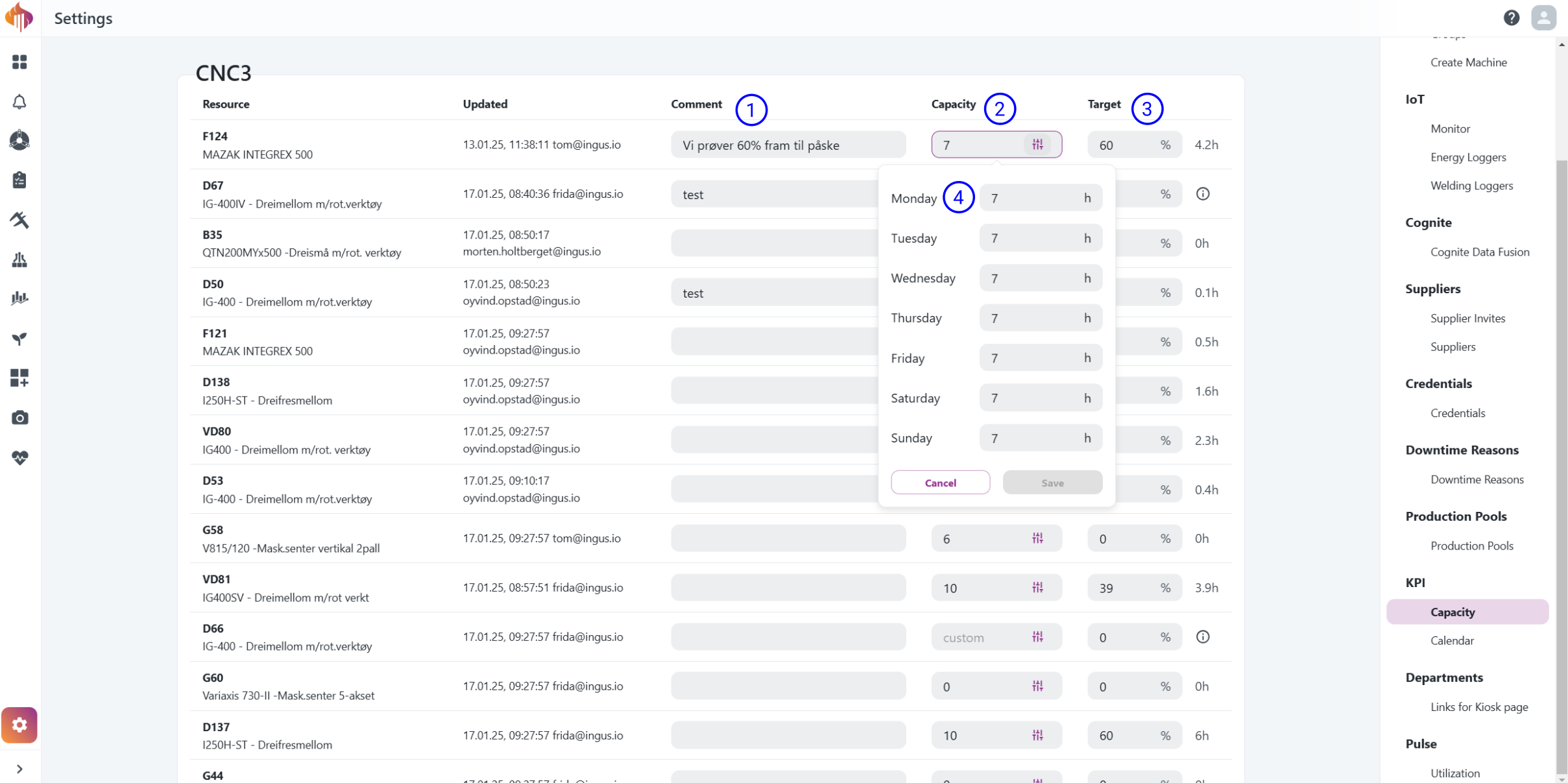
-
Comment: Add a comment to provide context for your decision.
-
Capacity: Set hourly capacity per resource for each day, or all days at once.
-
Target: Define the target utilization percentage per resource.
-
Capacity days: Different capacities can be set for different days.
⚠️ Admin Tip:
Avoid entering very small non-zero capacities (for example, 0.1 h) on days when no production is planned.
Such values can lead to extremely high utilization percentages if even minimal work is registered.
If the machine should not be active, set its capacity to 0 h for those days.
Factory Calendar settings
Factory calendar settings are only available for Admins and can be accessed in the bottom-left corner if you have the Admin role.
The factory calendar defines the baseline working hours for the entire site, including normal weekly hours, holidays, and half-days. These settings serve as the foundation for OEE calculations.
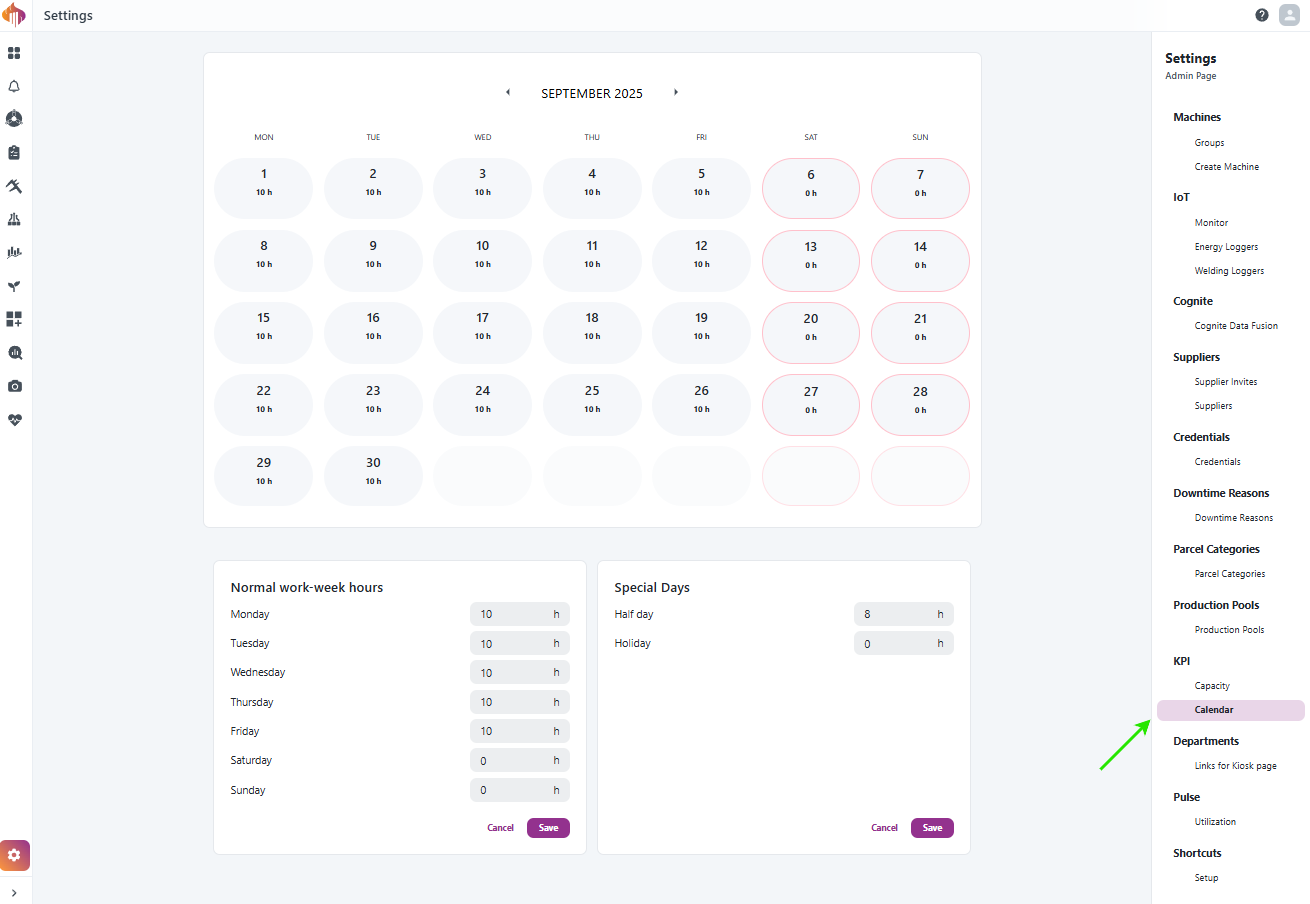
Descriptions:
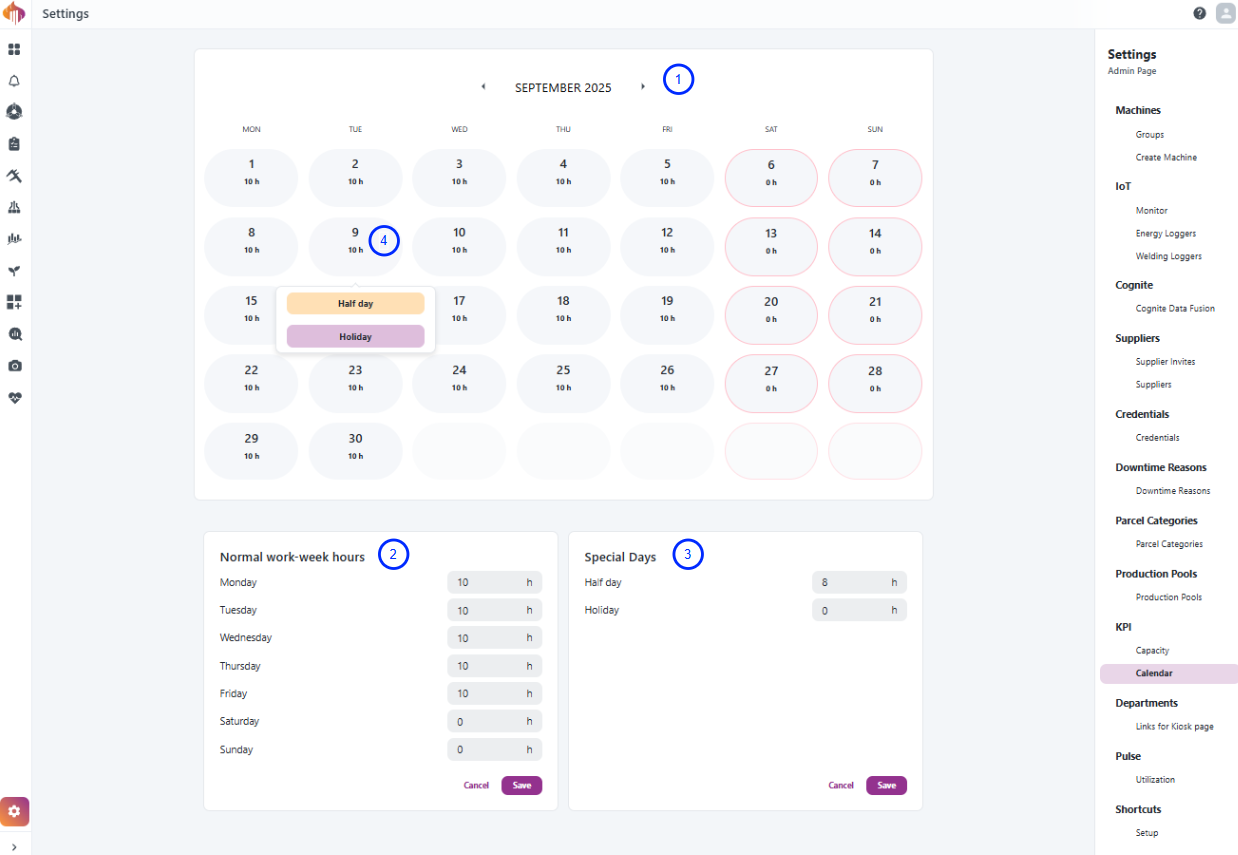
-
Calendar view: Shows configured hours per day for the selected month. Special days (half days, holidays) gets highlighted.
-
Normal work-week hours: Define the standard expected hours per weekday (e.g., Mon–Fri 10h, Sat/Sun 0h).
-
Special days: Configure exceptions such as half days or holidays. These override the normal weekly hours.
-
Overrides: Apply special rules directly in the calendar view (e.g., mark a specific date as a holiday).
Downtime Reason widget
The Downtime Reason widget simplifies reporting of downtime reasons significantly.
This widget lets you select between downtime topics and start reporting. This way, users can easily report downtime without having to report through the Resource Activity Timeline.
How to report a state:

How to use:
- Make sure you have a resource selected in your workspace, or select a static resource for the widget in the top left corner.
- Select a downtime topic and optionally add a comment.
- If the resource records machine states, you can choose to mark Cancel on machine state change. This will automatically stop reporting when the machine state changes.
- Click report to start the reporting process.
- If Cancel on machine state change is not selected, the reporting will stop when you click the stop button.
Downtime Duration widget
The Downtime Duration widget gives a quick, at-a-glance view of reported downtime reasons and their total duration, based on your selected resource and time range.
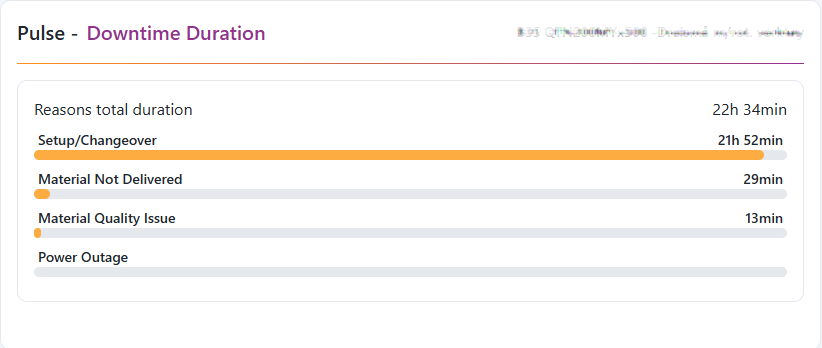
Resource Activity Timeline widget
The Resource Activity Timeline is availble as a widget in workspace. Watch demo here.